Cloning and characterization of hSRP1 gamma, a tissue-specific nuclear transport factor
- PMID: 9435235
- PMCID: PMC18463
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.2.582
Cloning and characterization of hSRP1 gamma, a tissue-specific nuclear transport factor
Abstract
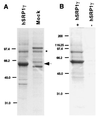
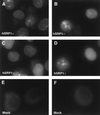
Nuclear import of proteins containing a nuclear localization signal (NLS) is dependent on the presence of a cytoplasmic NLS receptor, the GTPase Ran, and p10/ NTF2. The NLS receptor is a heterodimeric proteins consisting of subunits of approximately 60 and 97 kDa, which have been termed importin alpha/beta, karyopherin alpha/beta, or PTAC 58/ 97. Members of the 60-kDa/importin alpha subunit family directly bind to the NLS motif and have been shown to function as adaptors that tether NLS-containing proteins to the p97/ importin beta subunit and to the downstream transport machinery. Herein we report the identification and characterization of hSRP1 gamma, a human importin alpha homologue. The hSRP1 gamma protein is around 45% identical to the previously identified human importin alpha homologues hSRP1 alpha/Rch1 and NPI/ hSRP1. hSRP1 gamma can form a complex with importin beta and is able to mediate import of a BSA-NLS substrate in an in vitro nuclear import system. Interestingly, hSRP1 gamma shows a very selective expression pattern and is most abundantly expressed in skeletal muscle, representing more than 1% of the total protein in this tissue. A potential role for hSRP1 gamma in tissue-specific transport events is discussed.
Figures

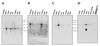

References
-
- Davis L I. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:865–896. - PubMed
-
- Doye V, Hurt E. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:401–411. - PubMed
-
- Pante N, Aebi U. J Cell Sci (Suppl) 1995;19:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg M W, Allen T D. Curr Biol. 1995;7:301–309. - PubMed
-
- Dingwall C, Laskey R A. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991;16:478–481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

