Fc receptors are required in passive and active immunity to melanoma
- PMID: 9435247
- PMCID: PMC18475
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.2.652
Fc receptors are required in passive and active immunity to melanoma
Abstract
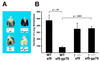
Effective tumor immunity requires recognition of tumor cells coupled with the activation of host effector responses. Fc receptor (FcR) gamma-/- mice, which lack the activating Fc gamma R types I and III, did not demonstrate protective tumor immunity in models of passive and active immunization against a relevant tumor differentiation antigen, the brown locus protein gp75. In wild-type mice, passive immunization with mAb against gp75 or active immunization against gp75 prevented the development of lung metastases. This protective response was completely abolished in FcR gamma-deficient mice. Immune responses were intact in gamma-/- mice because IgG titers against gp75 develop normally in gamma-/- mice immunized with gp75. However, uncoupling of the Fc gamma R effector pathway from antibody recognition of tumor antigens resulted in a loss of protection against tumor challenge. These data demonstrate an unexpected and critical role for FcRs in mediating tumor cytotoxicity in vivo and suggest that enhancement of Fc gamma R-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity by inflammatory cells is a key step in the development of effective tumor immunotherapeutics.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

