Morphology of the yeast endocytic pathway
- PMID: 9436999
- PMCID: PMC25237
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.1.173
Morphology of the yeast endocytic pathway
Abstract
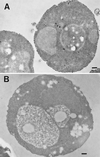
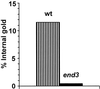
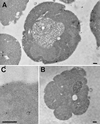
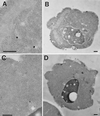
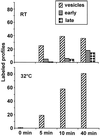
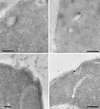
Positively charged Nanogold (Nanoprobes, Stony Brook, NY) has been developed as a new marker to follow the endocytic pathway in yeast. Positively charged Nanogold binds extensively to the surface of yeast spheroplasts and is internalized in an energy-dependent manner. Internalization of gold is blocked in the end3 mutant. During a time course of incubation of yeast spheroplasts with positively charged Nanogold at 15 degrees C, the gold was detected sequentially in small vesicles, a peripheral, vesicular/tubular compartment that we designate as an early endosome, a multivesicular body corresponding to the late endosome near the vacuole, and in the vacuole. Experiments examining endocytosis in the sec18 mutant showed an accumulation of positively charged Nanogold in approximately 30-50 nm diameter vesicles. These vesicles most likely represent the primary endocytic vesicles as no other intermediates were detected in the mutant cells, and they correspond in size to the first vesicles detected in wild-type spheroplasts at 15 degrees C. These data lend strong support to the idea that the internalization step of endocytosis in yeast involves formation of small vesicles of uniform size from the plasma membrane.
Figures


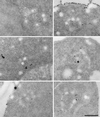
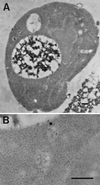
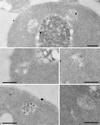
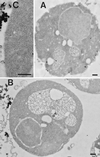
Similar articles
-
A new vital stain for visualizing vacuolar membrane dynamics and endocytosis in yeast.J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(5):779-92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.5.779. J Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7533169 Free PMC article.
-
Ordering of compartments in the yeast endocytic pathway.Traffic. 2002 Jan;3(1):37-49. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2002.30106.x. Traffic. 2002. PMID: 11872141
-
Role of endoplasmic reticulum-derived vesicles in the formation of Golgi elements in sec23 and sec18 Saccharomyces Cerevisiae mutants.Anat Rec. 1998 Jun;251(2):256-64. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(199806)251:2<256::AID-AR15>3.0.CO;2-N. Anat Rec. 1998. PMID: 9624457
-
The yeast endocytic membrane transport system.Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Dec 15;51(6):547-62. doi: 10.1002/1097-0029(20001215)51:6<547::AID-JEMT5>3.0.CO;2-D. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 11169857 Review.
-
Multivesicular bodies and multivesicular endosomes: the "ins and outs" of endosomal traffic.Sci STKE. 2002 Jul 16;2002(141):pe32. doi: 10.1126/stke.2002.141.pe32. Sci STKE. 2002. PMID: 12122203 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthetic histidine-rich peptides inhibit Candida species and other fungi in vitro: role of endocytosis and treatment implications.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Aug;50(8):2797-805. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00411-06. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16870774 Free PMC article.
-
Electron microscopy for ultrastructural analysis and protein localization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microb Cell. 2015 Oct 12;2(11):412-428. doi: 10.15698/mic2015.11.237. Microb Cell. 2015. PMID: 28357267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanogold labeling of the yeast endosomal system for ultrastructural analyses.J Vis Exp. 2014 Jul 14;(89):51752. doi: 10.3791/51752. J Vis Exp. 2014. PMID: 25046212 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of receptor-mediated endocytosis in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Mar;10(3):799-817. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.3.799. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10069819 Free PMC article.
-
A eukaryotic capsular polysaccharide is synthesized intracellularly and secreted via exocytosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Dec;17(12):5131-40. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-08-0701. Epub 2006 Oct 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 17021252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dulic V, Egerton M, Elguindi I, Raths S, Singer B, Riezman H. Yeast endocytosis assays. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:697–710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

