An open rectifier potassium channel with two pore domains in tandem cloned from rat cerebellum
- PMID: 9437008
- PMCID: PMC6792778
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-03-00868.1998
An open rectifier potassium channel with two pore domains in tandem cloned from rat cerebellum
Abstract
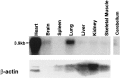
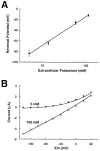
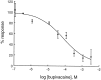
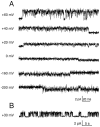
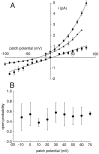
Tandem pore domain K+ channels represent a new family of ion channels involved in the control of background membrane conductances. We report the structural and functional properties of a TWIK-related acid-sensitive K+ channel (rTASK), a new member of this family cloned from rat cerebellum. The salient features of the primary amino acid sequence include four putative transmembrane domains and, unlike other cloned tandem pore domain channels, a PDZ (postsynaptic density protein, disk-large, zo-1) binding sequence at the C terminal. rTASK has distant overall homology to a putative Caenorhabditis elegans K+ channel and to the mammalian clones TREK-1 and TWIK-1. rTASK expression is most abundant in rat heart, lung, and brain. When exogenously expressed in Xenopus oocytes, rTASK currents activate instantaneously, are noninactivating, and are not gated by voltage. Because rTASK currents satisfy the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz current equation for an open channel, rTASK can be classified an open rectifier. Activation of protein kinase A produces inhibition of rTASK, whereas activation of protein kinase C has no effect. rTASK currents were inhibited by extracellular acidity. rTASK currents also were inhibited by Zn2+ (IC50 = 175 microM), the local anesthetic bupivacaine (IC50 = 68 microM), and the anti-convulsant phenytoin ( approximately 50% inhibition at 200 microM). By demonstrating open rectification and open probability independent of voltage, we have established that rTASK is a baseline potassium channel.
Figures




References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Andrews RJ, Bringas JR, Alonzo G. Cerebrospinal fluid pH and PCO2 rapidly follow arterial blood pH and PCO2 with changes in ventilation. Neurosurgery. 1994;34:466–470. - PubMed
-
- Assaf SY, Chung SH. Release of endogenous Zn2+ from brain tissue during activity. Nature. 1984;308:734–736. - PubMed
-
- Brenman JE, Chao DS, Gee SH, McGee AW, Craven SE, Santillano DR, Wu Z, Huang F, Xia H, Peters MF, Froehner SC, Bredt DS. Interaction of nitric oxide synthase with the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 and alpha1-syntrophin mediated by PDZ domains. Cell. 1996;84:757–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
