Interaction of presenilins with the filamin family of actin-binding proteins
- PMID: 9437013
- PMCID: PMC2042137
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-03-00914.1998
Interaction of presenilins with the filamin family of actin-binding proteins
Abstract
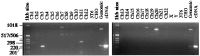
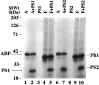
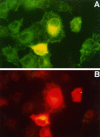
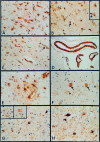
Mutations in presenilin genes PS1 and PS2 account for approximately 50% of early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD). The PS1 and PS2 genes encode highly homologous transmembrane proteins related to the Caenorhabditis elegans sel-12 and spe-4 gene products. A hydrophilic loop region facing the cytoplasmic compartment is likely to be functionally important because at least 14 mutations in FAD patients have been identified in this region. We report here that the loop regions of PS1 and PS2 interact with nonmuscle filamin (actin-binding protein 280, ABP280) and a structurally related protein (filamin homolog 1, Fh1). Overexpression of PS1 appears to modify the distribution of ABP280 and Fh1 proteins in cultured cells. A monoclonal antibody recognizing ABP280 and Fh1 binds to blood vessels, astrocytes, neurofibrillary tangles, neuropil threads, and dystrophic neurites in the AD brain. Detection of ABP280/Fh1 proteins in these structures suggests that these presenilin-interacting proteins may be involved in the development of AD and that interactions between presenilins and ABP280/Fh1 may be functionally significant. The ABP280 gene is located on the human X chromosome, whereas the newly identified Fh1 gene maps to human chromosome 3. These results provide a new basis for understanding the function of presenilin proteins and further implicate cytoskeletal elements in AD pathogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Berg L, McKeel DW, Jr, Miller JP, Baty J. Neuropathologic indexes of Alzheimer’s disease in demented and nondemented people aged 80 years and older. Arch Neurol. 1993;50:349–358. - PubMed
-
- Brown KD, Binder LI. Identification of the intermediate filament-associated protein gyronemin as filamin, implication for a novel mechanism of cytoskeletal interaction. J Cell Sci. 1992;102:19–30. - PubMed
-
- Cai X-D, Golde TE, Younkin SG. Release of excess amyloid β protein from a mutant amyloid β protein precursor. Science. 1993;259:514–516. - PubMed
-
- Chartier-Harlin M-C, Parfitt M, Legrain S, Perez-Tur J, Brousseau T, Evans A, Berr C, Vidal O, Roques P, Gourlet V, Delacourte A, Rossor M, Amouyel P. Apolipoprotein E ε4 allele as a major risk factor for sporadic early and late-onset forms of Alzheimer’s disease: analysis of the 19q13.2 chromosomal region. Hum Mol Genet. 1994;3:569–574. - PubMed
-
- Citron M, Oltersdorf T, Haass C, McConlogue L, Hung AY, Seubert P, Vigo-Pelfry C, Lieberburg I, Selkoe DJ. Mutation of the β-amyloid precursor protein in familial Alzheimer’s disease increases β-protein production. Nature. 1992;360:672–674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
