Variability and correlated noise in the discharge of neurons in motor and parietal areas of the primate cortex
- PMID: 9437036
- PMCID: PMC6792758
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-03-01161.1998
Variability and correlated noise in the discharge of neurons in motor and parietal areas of the primate cortex
Abstract
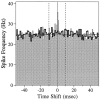
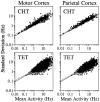
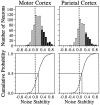
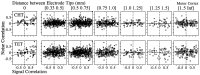
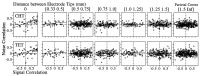
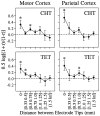
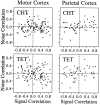
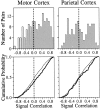
We analyzed the magnitude and interneuronal correlation of the variability in the activity of single neurons that were recorded simultaneously using a multielectrode array in the primary motor cortex and parietal areas 2/5 in rhesus monkeys. The animals were trained to move their arms in one of eight directions as instructed by a visual target. The relationship between variability (SD) and mean of the discharge rate was described by a power function with a similar exponent ( approximately 0.57), regardless of the cortical area or the behavioral condition. We examined whether the deviation from mean activity between target onset and the end of the movement was correlated on a trial-by-trial basis with variability in activity during the hold period before target onset. In both cortical areas, for about a quarter of the neurons, the neuronal noise of these two periods was positively correlated, whereas significant negative correlations were seldom observed. Overall, neurons with higher signal correlation (i.e., similar directional pattern) showed higher noise correlation in both cortical areas. On the other hand, when the data were divided according to the distance between the electrode tips from which the neurons were recorded, a consistent relationship between the signal and noise correlations was found only for pairs of neurons recorded through the same electrode. These results suggest that nearby neurons with similar directional tuning carry primarily redundant messages, whereas neurons in separate cortical columns perform more independent processing.
Figures

References
-
- Aldridge JW, Gilman S. The temporal structure of spike trains in the primate basal ganglia: afferent regulation of bursting demonstrated with precentral cerebral ablation. Brain Res. 1991;543:123–138. - PubMed
-
- Amirikian B, Georgopoulos AP. Motor cortical organization of preferred directions. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 1997;23:1555.
-
- Arieli A, Sterkin A, Grinvald A, Aetsen A. Dynamics of ongoing activity: explanation of the large variability in evoked cortical responses. Science. 1996;273:1868–1871. - PubMed
-
- Ashe J, Georgopoulos AP. Movement parameters and neural activity in motor cortex and area 5. Cereb Cortex. 1994;6:590–600. - PubMed
-
- Berman NJ, Douglas RJ, Martin KAC. GABA-mediated inhibition in the neural networks of visual cortex. In: Mize RR, Marc RE, Sillito AM, editors. Progress in brain research. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 1992. pp. 443–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
