Effect of Ca2+ channel blockers, external Ca2+ and phospholipase A2 inhibitors on t-butylhydroperoxide-induced lipid peroxidation and toxicity in rat liver slices
- PMID: 9439155
- PMCID: PMC4531990
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1997.12.2.193
Effect of Ca2+ channel blockers, external Ca2+ and phospholipase A2 inhibitors on t-butylhydroperoxide-induced lipid peroxidation and toxicity in rat liver slices
Abstract
Objectives: This study was undertaken to examine the effect of oxidant on lipid peroxidation and lethal cell injury in rat liver slices.
Methods: t-Butylhydroperoxide (t-BHP) was employed as a model of an oxidant. The lipid peroxidation and lethal cell injury were estimated by measuring the formation of malondialdehyde (MDA) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release, respectively.
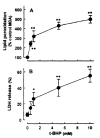
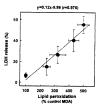
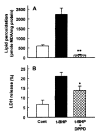
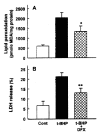
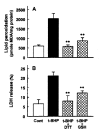
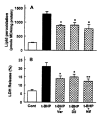
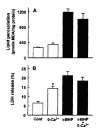
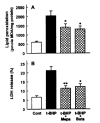
Results: t-BHP increased lipid peroxidation and LDH release in a dose-dependent manner over concentrations of 0.5-10 mM. t-BHP-induced lipid peroxidation was completely prevented by an antioxidant, N,N-diphenyl-p-phenylenediamine (DPPD), but LDH release was partially decreased. Both t-BHP-induced lipid peroxidation and LDH release were significantly protected by iron chelator, deferoxamine, sulfhydryl reducing agent, dithiothreitol and glutathione. Ca2+ channel blockers, verapamil, diltiazem and nifedipine exerted a significant protective effect against t-BHP-induced lipid peroxidation and LDH release. By contrast, addition of external Ca2+ chelator, ethylene glycol bis(b-aminoethyl ether)-N,N-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) did not alter t-BHP-induced lipid peroxidation, whereas t-BHP-induced lethal cell injury was significantly prevented. Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) inhibitors, mepacrine and butacaine produced a partial protective effect.
Conclusions: These results suggest that t-BHP induces cell injury by lipid peroxidation-dependent and -independent mechanisms which can be partially prevented by Ca2+ channel blockers and PLA2 inhibitors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential effect of Ca2+ on oxidant-induced lethal cell injury and alterations of membrane functional integrity in renal cortical slices.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1996 Dec;141(2):607-16. doi: 10.1006/taap.1996.0327. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8975786
-
K(+)-linked release of oxidized glutathione induced by tert-butyl hydroperoxide in perfused rat liver is independent of lipid peroxidation and cell death.Jpn J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;65(3):183-91. doi: 10.1254/jjp.65.183. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 7799518
-
Effects of antioxidants and Ca2+ in cisplatin-induced cell injury in rabbit renal cortical slices.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1997 Oct;146(2):261-9. doi: 10.1006/taap.1997.8252. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9344894
-
Effect of extracellular ions and modulators of calcium transport on survival of tert-butyl hydroperoxide exposed cardiac myocytes.Cardiovasc Res. 1993 Oct;27(10):1873-81. doi: 10.1093/cvr/27.10.1873. Cardiovasc Res. 1993. PMID: 8275538
-
Mechanisms of cell toxicity.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;1(2):231-5. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90093-8. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989. PMID: 2698675 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The protection of hepatocyte cells from the effects of oxidative stress by treatment with vitamin E in conjunction with DTT.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:486267. doi: 10.1155/2010/486267. Epub 2010 May 18. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20490359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Floyd RA. Role of oxygen free radicals in carcinogenesis and brain ischemia. FASEB J. 1990;4:2587. - PubMed
-
- Freeman BA, Crapo JD. Biology of disease: Free radicals and tissue injury. Lab Invest. 1982;47:412. - PubMed
-
- Rush GF, Gorski JR, Ripple MG, Sominski J, Bugelski P, Hewitt WR. Organic hydroperoxide-induced lipid peroxidation and ceil death in isolated hypatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1985;78:473. - PubMed
-
- Bellomo G, Thor H, Orrenius S. Increased in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration during t-butyl hydroperoxide metabolism by isolated hepatocytes involves NADPH oxidation and mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ stores. FEBS Lett. 1982b;168:38. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
