A DnaK homolog in Myxococcus xanthus is involved in social motility and fruiting body formation
- PMID: 9440508
- PMCID: PMC106874
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.2.218-224.1998
A DnaK homolog in Myxococcus xanthus is involved in social motility and fruiting body formation
Abstract
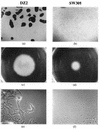
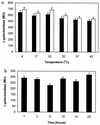
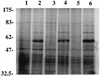
Myxococcus xanthus is a gram-negative soil bacterium which exhibits a complex life cycle and social behavior. In this study, two developmental mutants of M. xanthus were isolated through Tn5 transposon mutagenesis. The mutants were found to be defective in cellular aggregation as well as in sporulation. Further phenotypic characterization indicated that the mutants were defective in social motility but normal in directed cell movements. Both mutations were cloned by a transposon-tagging method. Sequence analysis indicated that both insertions occurred in the same gene, which encodes a homolog of DnaK. Unlike the dnaK genes in other bacteria, this M. xanthus homolog appears not to be regulated by temperature or heat shock and is constitutively expressed during vegetative growth and under starvation. The defects of the mutants indicate that this DnaK homolog is important for the social motility and development of M. xanthus.
Figures
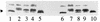


Similar articles
-
Phenotypic analyses of frz and dif double mutants of Myxococcus xanthus.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000 Nov 15;192(2):211-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09384.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000. PMID: 11064197
-
A chaperone in the HSP70 family controls production of extracellular fibrils in Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 1998 Oct;180(20):5357-68. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.20.5357-5368.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9765567 Free PMC article.
-
The Myxococcus xanthus wbgB gene encodes a glycosyltransferase homologue required for lipopolysaccharide O-antigen biosynthesis.Arch Microbiol. 2000 Dec;174(6):399-405. doi: 10.1007/s002030000226. Arch Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11195095
-
Gliding motility in bacteria: insights from studies of Myxococcus xanthus.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999 Sep;63(3):621-41. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.63.3.621-641.1999. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10477310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual regulation with Ser/Thr kinase cascade and a His/Asp TCS in Myxococcus xanthus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:111-21. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792684 Review.
Cited by
-
SigF, a new sigma factor required for a motility system of Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 2005 Dec;187(24):8537-41. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.24.8537-8541.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 16321963 Free PMC article.
-
Independence and interdependence of Dif and Frz chemosensory pathways in Myxococcus xanthus chemotaxis.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Aug;69(3):714-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06322.x. Epub 2008 Jun 28. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18554324 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular polysaccharides mediate pilus retraction during social motility of Myxococcus xanthus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Apr 29;100(9):5443-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0836639100. Epub 2003 Apr 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12704238 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic profiling of ABC transporter coding genes in Myxococcus xanthus.Front Microbiol. 2014 Jul 18;5:352. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00352. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25101061 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation of FrzCD defines a discrete step in the developmental program of Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 1998 Nov;180(21):5765-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.21.5765-5768.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9791131 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

