Identification of the rrmA gene encoding the 23S rRNA m1G745 methyltransferase in Escherichia coli and characterization of an m1G745-deficient mutant
- PMID: 9440525
- PMCID: PMC106891
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.2.359-365.1998
Identification of the rrmA gene encoding the 23S rRNA m1G745 methyltransferase in Escherichia coli and characterization of an m1G745-deficient mutant
Abstract
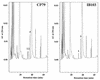
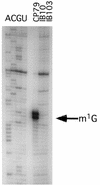
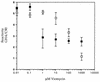
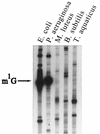
An Escherichia coli mutant lacking the modified nucleotide m1G in rRNA has previously been isolated (G. R. Björk and L. A. Isaksson, J. Mol. Biol. 51:83-100, 1970). In this study, we localize the position of the m1G to nucleotide 745 in 23S rRNA and characterize a mutant deficient in this modification. This mutant shows a 40% decreased growth rate in rich media, a drastic reduction in loosely coupled ribosomes, a 20% decreased polypeptide chain elongation rate, and increased resistance to the ribosome binding antibiotic viomycin. The rrmA gene encoding 23S rRNA m1G745 methyltransferase was mapped to bp 1904000 on the E. coli chromosome and identified to be identical to the previously sequenced gene yebH.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recognition of nucleotide G745 in 23 S ribosomal RNA by the rrmA methyltransferase.J Mol Biol. 2001 Jul 27;310(5):1001-10. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4836. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11501991
-
Sequence analysis and structure prediction of 23S rRNA:m1G methyltransferases reveals a conserved core augmented with a putative Zn-binding domain in the N-terminus and family-specific elaborations in the C-terminus.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 Jan;4(1):93-9. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 11763974
-
YccW is the m5C methyltransferase specific for 23S rRNA nucleotide 1962.J Mol Biol. 2008 Nov 14;383(3):641-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.08.061. Epub 2008 Aug 29. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18786544
-
The last rRNA methyltransferase of E. coli revealed: the yhiR gene encodes adenine-N6 methyltransferase specific for modification of A2030 of 23S ribosomal RNA.RNA. 2012 Sep;18(9):1725-34. doi: 10.1261/rna.034207.112. Epub 2012 Jul 30. RNA. 2012. PMID: 22847818 Free PMC article.
-
The rlmB gene is essential for formation of Gm2251 in 23S rRNA but not for ribosome maturation in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2001 Dec;183(23):6957-60. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.23.6957-6960.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11698387 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ketolide antimicrobial activity persists after disruption of interactions with domain II of 23S rRNA.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Oct;48(10):3677-83. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.10.3677-3683.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15388419 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of 23S rRNA hairpin 35 and its interaction with the tylosin-resistance methyltransferase RlmAII.EMBO J. 2003 Jan 15;22(2):183-92. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg022. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12514124 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of an essential Escherichia coli GTPase, Der, with the 50S ribosome via the KH-like domain.J Bacteriol. 2010 Apr;192(8):2277-83. doi: 10.1128/JB.00045-10. Epub 2010 Feb 19. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20172997 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond a Ribosomal RNA Methyltransferase, the Wider Role of MraW in DNA Methylation, Motility and Colonization in Escherichia coli O157:H7.Front Microbiol. 2019 Nov 13;10:2520. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02520. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31798540 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics and evolution of proteins involved in RNA metabolism.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Apr 1;30(7):1427-64. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.7.1427. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11917006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berlyn M K B, Low K B, Rudd K E. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 9. In: Neidhardt F C, Curtiss III R, Ingraham J L, Lin E C C, Low K B, Magasanik B, Reznikoff W S, Riley M, Schaechter M, Umbarger H E, editors. Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology. 2nd ed. Washington, D.C: ASM Press; 1996. pp. 1715–1902.
-
- Björk G R. Stable RNA modifications. In: Neidhardt F C, Curtiss III R, Ingraham J L, Lin E C C, Low K B, Magasanik B, Reznikoff W S, Riley M, Schaechter M, Umbarger H E, editors. Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology. 2nd ed. Washington, D.C: ASM Press; 1996. pp. 861–886.
-
- Björk G R, Isaksson L A. Isolation of mutants of Escherichia coli lacking 5-methyluracil in transfer ribonucleic acid or 1-methylguanine in ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1970;51:83–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

