Construction and characterization of a Helicobacter pylori clpB mutant and role of the gene in the stress response
- PMID: 9440536
- PMCID: PMC106902
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.2.426-429.1998
Construction and characterization of a Helicobacter pylori clpB mutant and role of the gene in the stress response
Abstract
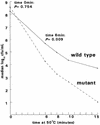
Antiserum raised against whole Helicobacter pylori cells identified a novel 94-kDa antigen. The nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the 94-kDa antigen was determined, and analysis of the deduced amino acid sequence revealed structural features typical of the ClpB ATPase family of stress response proteins. An isogenic H. pylori clpB mutant showed increased sensitivity to high-temperature stress, indicating that the clpB gene product functions as a stress response protein in H. pylori.
Figures

References
-
- Blaser M J. Helicobacter pylori: its role in disease. Clin Infect Dis. 1992;15:386–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

