Nitric oxide inhibits rhinovirus-induced cytokine production and viral replication in a human respiratory epithelial cell line
- PMID: 9444985
- PMCID: PMC124563
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.2.934-942.1998
Nitric oxide inhibits rhinovirus-induced cytokine production and viral replication in a human respiratory epithelial cell line
Abstract
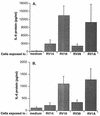
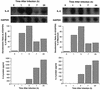
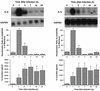
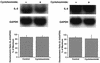
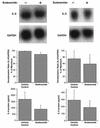
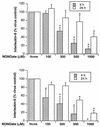
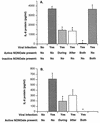
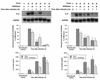
To better understand the early biochemical events that occur in human rhinovirus (HRV) infections, we examined the kinetics and mechanisms of interleukin-8 (IL-8) and IL-6 production from infected epithelial cells. Several HRV strains caused IL-8 and IL-6 production, but HRV-16 induced maximal IL-8 and IL-6 mRNA expression and protein production more rapidly than did HRV-14, despite similar rates of replication of the two viral strains. Viral induction of cytokine mRNA does not require new protein synthesis, since it was unaffected by cycloheximide treatment. The potent glucocorticoid budesonide did not affect viral replication or cytokine mRNA induction but modestly inhibited cytokine protein production. Interestingly, the nitric oxide donor 3-(2-hydroxy-2-nitroso-1-propylhydrazino)-1-propanamine (NONOate) inhibited both rhinovirus replication and cytokine production in a dose-dependent fashion without reducing levels of cytokine mRNA. The NONOate effects were due to release of nitric oxide, because NONOate that had been depleted of its nitric oxide content had no effect. Thus, nitric oxide may play an important anti-inflammatory and antiviral role in colds and nitric oxide donors may represent a novel therapeutic approach.
Figures

References
-
- Akiro S, Hirano T, Taga T, Kishimoto T. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF) FASEB J. 1990;4:2860–2867. - PubMed
-
- Arola M, Ziegler T, Puhakka H, Lehtonen O P, Ruuskanen O. Rhinovirus in otitis media with effusion. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1990;99:451–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

