Resistance to virus infection conferred by the interferon-induced promyelocytic leukemia protein
- PMID: 9444998
- PMCID: PMC124576
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.2.1043-1051.1998
Resistance to virus infection conferred by the interferon-induced promyelocytic leukemia protein
Abstract
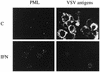
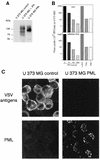
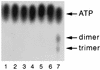
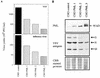
The interferon (IFN)-induced promyelocytic leukemia (PML) protein is specifically associated with nuclear bodies (NBs) whose functions are yet unknown. Two of the NB-associated proteins, PML and Sp100, are induced by IFN. Here we show that overexpression of PML and not Sp100 induces resistance to infections by vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) (a rhabdovirus) and influenza A virus (an orthomyxovirus) but not by encephalomyocarditis virus (a picornavirus). Inhibition of viral multiplication was dependent on both the level of PML expression and the multiplicity of infection and reached 100-fold. PML was shown to interfere with VSV mRNA and protein synthesis. Compared to the IFN mediator MxA protein, PML had less powerful antiviral activity. While nuclear body localization of PML did not seem to be required for the antiviral effect, deletion of the PML coiled-coil domain completely abolished it. Taken together, these results suggest that PML can contribute to the antiviral state induced in IFN-treated cells.
Figures



References
-
- Alber D, Staeheli P. Partial inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus by the interferon-induced human 9-27 protein. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1996;16:375–380. - PubMed
-
- Arnheiter H, Meier E. Mx proteins: antiviral proteins by chance or by necessity. New Biol. 1990;2:851–857. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee A K, Chattopadhyay D. Structure and function of the RNA polymerase of vesicular stomatitis virus. Adv virus Res. 1990;38:99–124. - PubMed
-
- Barlow P N, Luisi B, Milner A, Elliott M, Everett R. Structure of the C3HC4 domain by 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. A new structural class of zinc-finger. J Mol Biol. 1994;237:201–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

