Entry of amphotropic and 10A1 pseudotyped murine retroviruses is restricted in hematopoietic stem cell lines
- PMID: 9445044
- PMCID: PMC124622
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.2.1424-1430.1998
Entry of amphotropic and 10A1 pseudotyped murine retroviruses is restricted in hematopoietic stem cell lines
Abstract
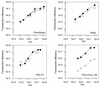
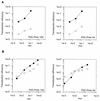
Although transduction with amphotropic murine leukemia virus (MLV) vectors has been optimized successfully for hematopoietic differentiated progenitors, gene transfer to early hematopoietic cells (stem cells) is still highly restricted. A similar restriction to gene transfer was observed in the mouse stem cell line FDC-Pmix compared with transfer in the more mature myeloid precursor cell line FDC-P1 and the human erythroleukemia cell line K562. Gene transfer was not improved when the vector was pseudotyped with gp70SU of the 10A1 strain of MLV, which uses the receptor of the gibbon ape leukemia virus (Pit1), in addition to the amphotropic receptor (Pit2). Although 10A1 and amphotropic gp70SU bound to FDC-P1, K562, and fibroblasts, no binding to FDC-Pmix cells was detected. This indicates that FDC-Pmix cells lack functional Pit2 and Pit1 receptors. Pseudotyping with the vesicular stomatitis virus G protein improved transduction efficiency in FDC-Pmix stem cells by 2 orders of magnitude, to fibroblast levels, confirming a block to retroviral infection at the receptor level.
Figures




References
-
- Agrawal Y P, Agrawal R S, Sinclair A M, Young D, Maruyama M, Levine F, Ho A D. Cell-cycle kinetics and VSV-G pseudotyped retroviral-mediated gene transfer in blood-derived CD34+ cells. Exp Hematol. 1996;24:738–747. - PubMed
-
- Baum, C., C. Stocking, T. Wagener, H.-G. Eckert, and W. Ostertag. Gene transfer and transgene expression in hematopoietic cells. In M. Strauss and W. Barranger (ed.), Concepts of gene therapy, in press. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, Germany.
-
- Beck-Engeser G, Stocking C, Just U, Albritton L, Dexter M, Spooncer E, Ostertag W. Retroviral vectors related to the myeloproliferative sarcoma virus allow efficient expression in hematopoietic stem and precursor cell lines, but retroviral infection is reduced in more primitive cells. Hum Gene Ther. 1991;2:61–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

