Structural localization of the E3 glycoprotein in attenuated Sindbis virus mutants
- PMID: 9445057
- PMCID: PMC124635
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.2.1534-1541.1998
Structural localization of the E3 glycoprotein in attenuated Sindbis virus mutants
Abstract
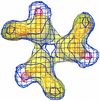
We have determined the three-dimensional structures of the wild-type Sindbis virus and two of its mutants that retain the E3 sequence within PE2. Using difference imaging between these mutants and the wild-type virus, we have assigned a location for the 64-amino-acid sequence corresponding to E3 in the mutant spike complex. In the wild-type virus, the spike is composed of an E1-E2 heterotrimer. The E3 protein was found to protrude midway between the center of the spike complex and the tips. Based on these results and the work of others, we propose a distribution for the functional domains of the spike proteins within the structure of wild-type Sindbis virus. Within the structure of the virus, the E1 domains form the central portion of the spike complex, while the tips are formed by the E2 domains that flare out from the center of the complex. The structural similarity between these Sindbis virus mutants and Ross River virus suggests that E3 may also be present in the latter, which is also a member of the Alphavirus genus.
Figures
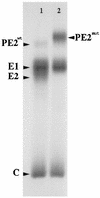

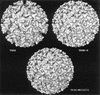

Similar articles
-
Mutating conserved cysteines in the alphavirus e2 glycoprotein causes virus-specific assembly defects.J Virol. 2012 Mar;86(6):3100-11. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06615-11. Epub 2012 Jan 11. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22238319 Free PMC article.
-
Role of conserved cysteines in the alphavirus E3 protein.J Virol. 2009 Mar;83(6):2584-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02158-08. Epub 2008 Dec 24. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19109378 Free PMC article.
-
Disulfide bridge-mediated folding of Sindbis virus glycoproteins.J Virol. 1996 Aug;70(8):5541-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.8.5541-5547.1996. J Virol. 1996. PMID: 8764067 Free PMC article.
-
Sindbis virus attachment: isolation and characterization of mutants with impaired binding to vertebrate cells.J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3363-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.67.6.3363-3374.1993. J Virol. 1993. PMID: 7684466 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of a functional HCV glycoprotein heterodimer.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2007 Jul;9(2):71-86. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17489436 Review.
Cited by
-
Virus maturation.Annu Rev Biophys. 2012;41:473-96. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-042910-155407. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Annu Rev Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22404678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The structure of Sindbis virus produced from vertebrate and invertebrate hosts as determined by small-angle neutron scattering.J Virol. 2010 May;84(10):5270-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00044-10. Epub 2010 Mar 10. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20219936 Free PMC article.
-
The surface conformation of Sindbis virus glycoproteins E1 and E2 at neutral and low pH, as determined by mass spectrometry-based mapping.J Virol. 2000 Jun;74(12):5667-78. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.12.5667-5678.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10823875 Free PMC article.
-
4.4 Å cryo-EM structure of an enveloped alphavirus Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus.EMBO J. 2011 Aug 9;30(18):3854-63. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.261. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21829169 Free PMC article.
-
Structural differences observed in arboviruses of the alphavirus and flavivirus genera.Adv Virol. 2014;2014:259382. doi: 10.1155/2014/259382. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Adv Virol. 2014. PMID: 25309597 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anthony R P, Paredes A M, Brown D T. Disulfide bonds are essential for the stability of the Sindbis virus envelope. Virology. 1992;190:330–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

