Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax requires direct access to DNA for recruitment of CREB binding protein to the viral promoter
- PMID: 9447968
- PMCID: PMC108783
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.2.721
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax requires direct access to DNA for recruitment of CREB binding protein to the viral promoter
Abstract
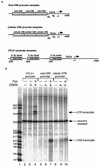
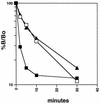
Efficient human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) replication and viral gene expression are dependent upon the virally encoded oncoprotein Tax. To activate HTLV-1 transcription, Tax interacts with the cellular DNA binding protein cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein (CREB) and recruits the coactivator CREB binding protein (CBP), forming a nucleoprotein complex on the three viral cyclic AMP-responsive elements (CREs) in the HTLV-1 promoter. Short stretches of dG-dC-rich (GC-rich) DNA, immediately flanking each of the viral CREs, are essential for Tax recruitment of CBP in vitro and Tax transactivation in vivo. Although the importance of the viral CRE-flanking sequences is well established, several studies have failed to identify an interaction between Tax and the DNA. The mechanistic role of the viral CRE-flanking sequences has therefore remained enigmatic. In this study, we used high resolution methidiumpropyl-EDTA iron(II) footprinting to show that Tax extended the CREB footprint into the GC-rich DNA flanking sequences of the viral CRE. The Tax-CREB footprint was enhanced but not extended by the KIX domain of CBP, suggesting that the coactivator increased the stability of the nucleoprotein complex. Conversely, the footprint pattern of CREB on a cellular CRE lacking GC-rich flanking sequences did not change in the presence of Tax or Tax plus KIX. The minor-groove DNA binding drug chromomycin A3 bound to the GC-rich flanking sequences and inhibited the association of Tax and the Tax-CBP complex without affecting CREB binding. Tax specifically cross-linked to the viral CRE in the 5'-flanking sequence, and this cross-link was blocked by chromomycin A3. Together, these data support a model where Tax interacts directly with both CREB and the minor-groove viral CRE-flanking sequences to form a high-affinity binding site for the recruitment of CBP to the HTLV-1 promoter.
Figures











References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
