Regulation of hypoxia-inducible mRNAs by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein requires binding to complexes containing elongins B/C and Cul2
- PMID: 9447969
- PMCID: PMC108784
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.2.732
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible mRNAs by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein requires binding to complexes containing elongins B/C and Cul2
Abstract
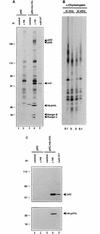
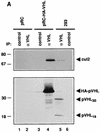
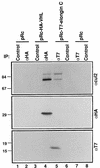
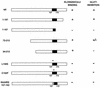
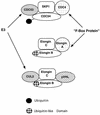
The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein (pVHL) binds to elongins B and C and posttranscriptionally regulates the accumulation of hypoxia-inducible mRNAs under normoxic (21% O2) conditions. Here we report that pVHL binds, via elongin C, to the human homolog of the Caenorhabditis elegans Cul2 protein. Coimmunoprecipitation and chromatographic copurification data suggest that pVHL-Cul2 complexes exist in native cells. pVHL mutants that were unable to bind to complexes containing elongin C and Cul2 were likewise unable to inhibit the accumulation of hypoxia-inducible mRNAs. A model for the regulation of hypoxia-inducible mRNAs by pVHL is presented based on the apparent similarity of elongin C and Cul2 to Skp1 and Cdc53, respectively. These latter proteins form complexes that target specific proteins for ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis.
Figures




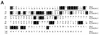
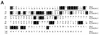


References
-
- Bai C, Sen P, Hofmann K, Ma L, Goebl M, Harper J W, Elledge S J. SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell. 1996;86:263–274. - PubMed
-
- Conaway, R. C., J. W. Conaway, and W. G. Kaelin, Jr. Unpublished data.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
