Frontoparietal cortical networks for directing attention and the eye to visual locations: identical, independent, or overlapping neural systems?
- PMID: 9448248
- PMCID: PMC33805
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.3.831
Frontoparietal cortical networks for directing attention and the eye to visual locations: identical, independent, or overlapping neural systems?
Abstract
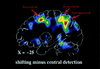
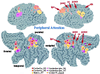
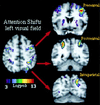
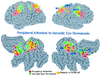
Functional anatomical and single-unit recording studies indicate that a set of neural signals in parietal and frontal cortex mediates the covert allocation of attention to visual locations, as originally proposed by psychological studies. This frontoparietal network is the source of a location bias that interacts with extrastriate regions of the ventral visual system during object analysis to enhance visual processing. The frontoparietal network is not exclusively related to visual attention, but may coincide or overlap with regions involved in oculomotor processing. The relationship between attention and eye movement processes is discussed at the psychological, functional anatomical, and cellular level of analysis.
Figures


References
-
- Ullman S. Cognition. 1984;18:97–159. - PubMed
-
- Eriksen C W, Hoffman J E. Percept Psychophys. 1972;12:201–204.
-
- Posner M I. Q J Exp Psychol. 1980;32:3–25. - PubMed
-
- Berlucchi G, Tassinari G, Marzi C A, Di Stefano M. Neuropsychologia. 1989;27:201–221. - PubMed
-
- Jonides J. In: Voluntary vs. Automatic Control over the Mind’s Eye’s Movement. Posner M I, Marin O, editors. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1981. pp. 187–205.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

