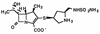In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of S-4661, a new carbapenem
- PMID: 9449267
- PMCID: PMC105462
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.1.94
In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of S-4661, a new carbapenem
Abstract
The in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of S-4661, a new 1beta-methylcarbapenem, were compared with those of imipenem, meropenem, biapenem, cefpirome, and ceftazidime. The activity of S-4661 against methicillin-susceptible staphylococci and streptococci was comparable to that of imipenem, with an MIC at which 90% of the strains tested were inhibited (MIC90) equal to 0.5 microg/ml or less. S-4661 was highly active against members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis, with MIC90s ranging from 0.032 to 0.5 microg/ml. Against imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, S-4661 was the most active among test agents (MIC90, 8 microg/ml). Furthermore, S-4661 displayed a high degree of activity against many ceftazidime-, ciprofloxacin-, and gentamicin-resistant isolates of P. aeruginosa. The in vivo efficacy of S-4661 against experimentally induced infections in mice caused by gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae and drug-resistant P. aeruginosa, reflected its potent in vitro activity and high levels in plasma in mice. We conclude that S-4661 is a promising new carbapenem for the treatment of infections caused by gram-positive and -negative bacteria, including penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae and drug-resistant P. aeruginosa.
References
-
- Edwards, J. R. 1995. Meropenem: a microbiological overview. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 36(Suppl. A):1–17. - PubMed
-
- Iso Y, Irie T, Nishino Y, Motokawa K, Nishitani Y. A novel 1β-methylcarbapenem antibiotic, S-4661: synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 2-(5-substituted pyrrolidin-3-ylthio)-1β-methlycarbapenems. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1996;49:199–209. - PubMed
-
- Japanese Society for Chemotherapy. Method for the determination of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of fastidious bacteria and anaerobic bacteria by microdilution method. Chemotherapy (Tokyo) 1993;41:183–189.
-
- Japanese Society for Chemotherapy. Method for the determination of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of aerobic bacteria by microbrothdilution method. Chemotherapy (Tokyo) 1990;38:102–105.
-
- Kahan J S, Kahan F M, Geogelman R, Currie S A, Jacson M, Stapley E O, Miller A K, Hendlin D, Mochales S, Hernandez S, Woodruff H B, Birnbaum J. Thienamycin, a new beta-lactam antibiotic. I. Discovery, taxonomy, isolation, and physical properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1979;32:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical