Interleukin 7 transgenic mice develop chronic colitis with decreased interleukin 7 protein accumulation in the colonic mucosa
- PMID: 9449719
- PMCID: PMC2212121
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.3.389
Interleukin 7 transgenic mice develop chronic colitis with decreased interleukin 7 protein accumulation in the colonic mucosa
Abstract
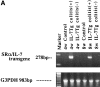
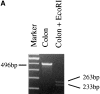
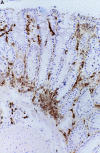
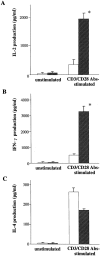
We have demonstrated that intestinal epithelial cells produce interleukin 7 (IL-7), and IL-7 serves as a potent regulatory factor for proliferation of intestinal mucosal lymphocytes expressing functional IL-7 receptor. To clarify the mechanism by which locally produced IL-7 regulates the mucosal lymphocytes, we investigated IL-7 transgenic mice. Here we report that transgenic mice expressing murine IL-7 cDNA driver by the SRalpha promoter developed chronic colitis in concert with the expression of SRalpha/IL-7 transgene in the colonic mucosa. IL-7 transgenic but not littermate mice developed chronic colitis at 4-12 wk of age, with histopathological similarity to ulcerative colitis in humans. Southern blot hybridization and competitive PCR demonstrated that the expression of IL-7 messenger RNA was increased in the colonic mucosal lymphocytes but not in the colonic epithelial cells. IL-7 protein accumulation was decreased in the goblet cell-depleted colonic epithelium in the transgenic mice. Immunohistochemical and cytokine production analysis showed that lymphoid infiltrates in the lamina propria were dominated by T helper cell type 1 CD4+ T cells. Flow cytometric analysis demonstrated that CD4+ intraepithelial T cells were increased, but T cell receptor gamma/delta T cells and CD8alpha/alpha cells were not increased in the area of chronic inflammation. Increased IL-7 receptor expression in mucosal lymphocytes was demonstrated in the transgenic mice. These findings suggest that chronic inflammation in the colonic mucosa may be mediated by dysregulation of colonic epithelial cell-derived IL-7, and this murine model of chronic colitis may contribute to the understanding of the pathogenesis of human inflammatory bowel disease.
Figures























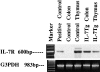
References
-
- Namen AE, Lupton S, Hjerrild K, Wignall J, Mochizuki DY, Schmierer AE, Mosley B, March CJ, Urdal DL, Gillis S, et al. Stimulation of B-cell progenitors by cloned murine interleukin-7. Nature. 1988;333:571–573. - PubMed
-
- Welch PA, Namen AE, Goodwin RG, Armitage R, Cooper MD. Human IL-7: a novel T cell growth factor. J Immunol. 1989;143:3562–3567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

