Induction of an antigen-specific, CD1-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte response In vivo
- PMID: 9449723
- PMCID: PMC2212129
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.3.433
Induction of an antigen-specific, CD1-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte response In vivo
Abstract
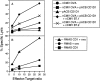
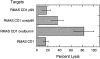
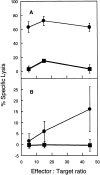
The majority of T cell responses are restricted to peptide antigens bound by polymorphic major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. However, peptide antigens can be presented to T cells by murine non-MHC-encoded CD1d (mCD1) molecules, and human T cell lines specific for nonpeptide antigens presented on CD1 isoforms have been identified. It is shown here that antigen-specific, mCD1-restricted lymphocytes can be generated in vivo by immunizing mice with a combination of plasmids encoding chicken ovalbumin, murine CD1d, and costimulatory molecules. Splenocytes from immunized mice have CD1d-restricted, MHC- unrestricted, ovalbumin-specific cytolytic activity that can be inhibited by anti-CD1 antibodies as well as a competing CD1-binding peptide. These results suggest a physiologic role for murine CD1d to present exogenous protein antigens.
Figures

References
-
- Porcelli SA. The CD1 family: a third lineage of antigen-presenting molecules. Adv Immunol. 1995;59:1–98. - PubMed
-
- Castano AR, Tangri S, Miller JE, Holcombe HR, Jackson MR, Huse WD, Kronenberg M, Peterson PA. Peptide binding and presentation by mouse CD1. Science. 1995;269:223–226. - PubMed
-
- Calabi F, Belt KT, Yu CY, Bradbury A, Mandy WJ, Milstein C. The rabbit CD1 and the evolutionary conservation of the CD1 gene family. Immunogenetics. 1989;30:370–377. - PubMed
-
- Calabi F, Jarvis JM, Martin L, Milstein C. Two classes of CD1 genes. Eur J Immunol. 1989;19:285–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

