Inscuteable and numb mediate asymmetric muscle progenitor cell divisions during Drosophila myogenesis
- PMID: 9450926
- PMCID: PMC316482
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.3.304
Inscuteable and numb mediate asymmetric muscle progenitor cell divisions during Drosophila myogenesis
Erratum in
- Genes Dev 1998 Apr 15;12(8):1241
Abstract
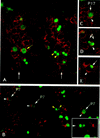
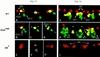
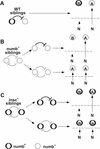
Each larval hemisegment comprises approximately 30 uniquely specified somatic muscles. These derive from muscle founders that arise as distinct sibling pairs from the division of muscle progenitor cells. We have analyzed the progenitor cell divisions of three mesodermal lineages that generate muscle (and pericardial cell) founders. Our results show that Inscuteable and Numb proteins are localized as cortical crescents on opposite sides of dividing progenitor cells. Asymmetric segregation of Numb into one of the sibling myoblasts depends on inscuteable and is essential for the specification of distinct sibling cell fates. Loss of numb or inscuteable results in opposite cell fate transformations-both prevent sibling myoblasts from adopting distinct identities, resulting in duplicated or deleted mesodermal structures. Our results indicate that the muscle progenitor cell divisions are intrinsically asymmetric; moreover, the involvement of both inscuteable and numb/N suggests that the specification of the distinct cell fates of sibling myoblasts requires intrinsic and extrinsic cues.
Figures



References
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas A, Matsuno K, Fortini ME. Notch signaling. Science. 1995;268:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Baker R, Schubiger G. Ectoderm induces muscle-specific gene expression in Drosophila embryos. Development. 1995;121:1387–1398. - PubMed
-
- Bate M. The embryonic development of larval muscles in Drosophila. Development. 1990;110:791–804. - PubMed
-
- ————— . The mesoderm and its derivatives. In: Bate M, Martínez-Arias A, editors. The development of Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1993. pp. 1013–1090.
-
- Bate, M., E. Rushton, and M. Frasch. 1993. A dual requirement for neurogenic genes in Drosophila myogenesis. Development (Suppl.) pp. 149–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
