Evidence that Spt4, Spt5, and Spt6 control transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 9450930
- PMCID: PMC316481
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.3.357
Evidence that Spt4, Spt5, and Spt6 control transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
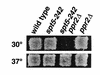
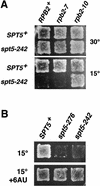
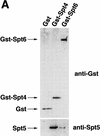
Previous characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Spt4, Spt5, and Spt6 proteins suggested that these proteins act as transcription factors that modify chromatin structure. In this work, we report new genetic and biochemical studies of Spt4, Spt5, and Spt6 that reveal a role for these factors in transcription elongation. We have isolated conditional mutations in SPT5 that can be suppressed in an allele-specific manner by mutations in the two largest subunits of RNA polymerase II (Pol II). Strikingly, one of these RNA Pol II mutants is defective for transcription elongation and the others cause phenotypes consistent with an elongation defect. In addition, we show that spt4, spt5, and spt6 mutants themselves have phenotypes suggesting defects in transcription elongation in vivo. Consistent with these findings, we show that Spt5 is physically associated with RNA Pol II in vivo, and have identified a region of sequence similarity between Spt5 and NusG, an Escherichia coli transcription elongation factor that binds directly to RNA polymerase. Finally, we show that Spt4 and Spt5 are tightly associated in a complex that does not contain Spt6. These results, taken together with the biochemical identification of a human Spt4-Spt5 complex as a transcription elongation factor (Wada et al. 1998), provide strong evidence that these factors are important for transcription elongation in vivo.
Figures
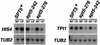



Similar articles
-
SPT4, SPT5 and SPT6 interactions: effects on transcription and viability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 1992 Oct;132(2):325-36. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.2.325. Genetics. 1992. PMID: 1330823 Free PMC article.
-
Spt5 and spt6 are associated with active transcription and have characteristics of general elongation factors in D. melanogaster.Genes Dev. 2000 Oct 15;14(20):2623-34. doi: 10.1101/gad.831900. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 11040216 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II elongation factors of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a targeted proteomics approach.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Oct;22(20):6979-92. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.20.6979-6992.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12242279 Free PMC article.
-
The Spt4-Spt5 complex: a multi-faceted regulator of transcription elongation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1829(1):105-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22982195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pleiotropic roles of SPT5 in transcription.Transcription. 2022 Feb-Jun;13(1-3):53-69. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2022.2103366. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Transcription. 2022. PMID: 35876486 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations in the transcription elongation factor SPT5 disrupt a reporter for dosage compensation in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(11):e1003073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003073. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23209435 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of mRNA cleavage/polyadenylation machinery by the yeast chromatin protein Sin1p/Spt2p.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 27;103(26):9808-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602014103. Epub 2006 Jun 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16788068 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal repeat domain of Spt5 plays an important role in suppression of Rad26-independent transcription coupled repair.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 19;285(8):5317-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.082818. Epub 2009 Dec 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20042611 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a regulator of transcription elongation as an accessory factor for the human Mediator coactivator.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Apr 10;104(15):6182-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608717104. Epub 2007 Apr 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17404243 Free PMC article.
-
Human Spt6 stimulates transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II in vitro.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Apr;24(8):3324-36. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.8.3324-3336.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15060154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, NY: Greene Publishing Associates/Wiley-Interscience; 1988.
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan C. Proceedings of the second international conference on intelligent systems for molecular biology. Menlo Park, CA: AAAI Press; 1994. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers; pp. 28–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
