Rabphilin-3A: a multifunctional regulator of synaptic vesicle traffic
- PMID: 9450942
- PMCID: PMC2222762
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.111.2.243
Rabphilin-3A: a multifunctional regulator of synaptic vesicle traffic
Abstract
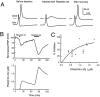
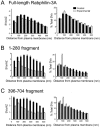
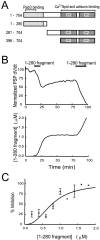
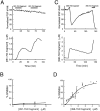
We have investigated the function of the synaptic vesicle protein Rabphilin-3A in neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. Presynaptic microinjection of recombinant Rabphilin-3A reversibly inhibited the exocytotic release of neurotransmitter. Injection of fragments of Rabphilin-3A indicate that at least two distinct regions of the protein inhibit neurotransmitter release: the NH2-terminal region that binds Rab3A and is phosphorylated by protein kinases and the two C2 domains that interact with calcium, phospholipid, and beta-adducin. Each of the inhibitory fragments and the full-length protein had separate effects on presynaptic morphology, suggesting that individual domains were inhibiting a subset of the reactions in which the full-length protein participates. In addition to inhibiting exocytosis, constructs containing the NH2 terminus of Rabphilin-3A also perturbed the endocytotic pathway, as indicated by changes in the membrane areas of endosomes, coated vesicles, and the plasma membrane. These results indicate that Rabphilin-3A regulates synaptic vesicle traffic and appears to do so at distinct stages of both the exocytotic and endocytotic pathways.
Figures


References
-
- Augustine GJ, Burns ME, DeBello WM, Pettit DL, Schweizer FE. Exocytosis: proteins and perturbations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1996;36:659–701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

