The Win1 mitotic regulator is a component of the fission yeast stress-activated Sty1 MAPK pathway
- PMID: 9450957
- PMCID: PMC25255
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.2.311
The Win1 mitotic regulator is a component of the fission yeast stress-activated Sty1 MAPK pathway
Abstract
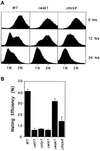
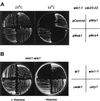
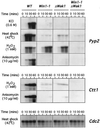
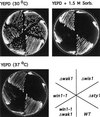
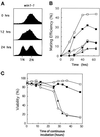
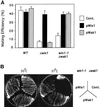
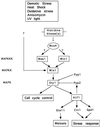
The fission yeast Sty1 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase (MAPK) and its activator the Wis1 MAP kinase kinase (MAPKK) are required for cell cycle control, initiation of sexual differentiation, and protection against cellular stress. Like the mammalian JNK/SAPK and p38/CSBP1 MAPKs, Sty1 is activated by a range of environmental insults including osmotic stress, hydrogen peroxide, UV light, menadione, heat shock, and the protein synthesis inhibitor anisomycin. We have recently identified two upstream regulators of the Wis1 MAPKK, namely the Wak1 MAPKKK and the Mcs4 response regulator. Cells lacking Mcs4 or Wak1, however, are able to proliferate under stressful conditions and undergo sexual differentiation, suggesting that additional pathway(s) control the Wis1 MAPKK. We now show that this additional signal information is provided, at least in part, by the Win1 mitotic regulator. We show that Wak1 and Win1 coordinately control activation of Sty1 in response to multiple environmental stresses, but that Wak1 and Win1 perform distinct roles in the control of Sty1 under poor nutritional conditions. Our results suggest that the stress-activated Sty1 MAPK integrates information from multiple signaling pathways.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Mcs4 response regulator coordinately controls the stress-activated Wak1-Wis1-Sty1 MAP kinase pathway and fission yeast cell cycle.Genes Dev. 1997 Apr 15;11(8):1008-22. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.8.1008. Genes Dev. 1997. PMID: 9136929
-
Evidence for a novel MAPKKK-independent pathway controlling the stress activated Sty1/Spc1 MAP kinase in fission yeast.J Cell Sci. 1998 Sep;111 ( Pt 18):2799-807. doi: 10.1242/jcs.111.18.2799. J Cell Sci. 1998. PMID: 9718372
-
Pyp1 and Pyp2 PTPases dephosphorylate an osmosensing MAP kinase controlling cell size at division in fission yeast.Genes Dev. 1995 Sep 1;9(17):2117-30. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.17.2117. Genes Dev. 1995. PMID: 7657164
-
Rad3 and Sty1 function in Schizosaccharomyces pombe: an integrated response to DNA damage and environmental stress?Mol Microbiol. 2008 Apr;68(2):246-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06147.x. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18366437 Review.
-
Nuclear roles and regulation of chromatin structure by the stress-dependent MAP kinase Sty1 of Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Nov;82(3):542-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07851.x. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21992435 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying the mitosis-meiosis decision.Chromosome Res. 2007;15(5):523-37. doi: 10.1007/s10577-007-1151-0. Chromosome Res. 2007. PMID: 17674143 Review.
-
Glycolytic enzyme GAPDH promotes peroxide stress signaling through multistep phosphorelay to a MAPK cascade.Mol Cell. 2008 Apr 11;30(1):108-13. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.01.017. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18406331 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic roles of the phospholipase B homolog Plb1 and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase Pka1 in the hypertonic stress response of Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Curr Genet. 2022 Dec;68(5-6):661-674. doi: 10.1007/s00294-022-01253-z. Epub 2022 Sep 16. Curr Genet. 2022. PMID: 36112198
-
Distinct regulatory proteins control the graded transcriptional response to increasing H(2)O(2) levels in fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Mar;13(3):805-16. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-06-0288. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 11907263 Free PMC article.
-
The stress-activated MAP kinase Sty1/Spc1 and a 3'-regulatory element mediate UV-induced expression of the uvi15(+) gene at the post-transcriptional level.Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Sep 1;28(17):3392-402. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.17.3392. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000. PMID: 10954610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basi G, Schmid E, Maundrell K. TATA box mutations in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe nmt1 promoter affect transcriptional efficiency but not the transcription start point or thiamine repressibility. Gene. 1993;123:131–136. - PubMed
-
- Brewster JL, de Valoir T, Dwyer ND, Winter E, Gustin MC. An osmosensing signal transduction pathway in yeast. Science. 1993;259:1760–1763. - PubMed
-
- Choi KY, Satterberg B, Lyons DM, Elion EA. Ste5 tethers multiple protein kinases in the MAP kinase cascade required for mating in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1994;78:499–512. - PubMed
-
- Corliss DA, White WEJ. Fluorescence of yeast vitally stained with ethidium bromide and propidium iodide. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981;29:45–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

