RhoA-dependent phosphorylation and relocalization of ERM proteins into apical membrane/actin protrusions in fibroblasts
- PMID: 9450964
- PMCID: PMC25270
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.2.403
RhoA-dependent phosphorylation and relocalization of ERM proteins into apical membrane/actin protrusions in fibroblasts
Abstract
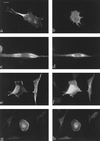
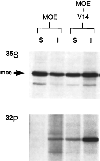
The ERM proteins (ezrin, radixin, and moesin) are a group of band 4. 1-related proteins that are proposed to function as membrane/cytoskeletal linkers. Previous biochemical studies have implicated RhoA in regulating the association of ERM proteins with their membrane targets. However, the specific effect and mechanism of action of this regulation is unclear. We show that lysophosphatidic acid stimulation of serum-starved NIH3T3 cells resulted in relocalization of radixin into apical membrane/actin protrusions, which was blocked by inactivation of Rho by C3 transferase. An activated allele of RhoA, but not Rac or CDC42Hs, was sufficient to induce apical membrane/actin protrusions and localize radixin or moesin into these structures in both Rat1 and NIH3T3 cells. Lysophosphatidic acid treatment led to phosphorylation of radixin preceding its redistribution into apical protrusions. Significantly, cotransfection of RhoAV14 or C3 transferase with radixin and moesin revealed that RhoA activity is necessary and sufficient for their phosphorylation. These findings reveal a novel function of RhoA in reorganizing the apical actin cytoskeleton and suggest that this function may be mediated through phosphorylation of ERM proteins.
Figures








References
-
- Aktories K, Braun U, Rosener S, Just I, Hall A. The rho gene product expressed in E. coli is a substrate of ADP-ribosyltransferase C3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989;158:209–213. - PubMed
-
- Amano M, Chihara K, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Nakamura N, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions enhanced by Rho- kinase. Science. 1997;275:1308–1311. - PubMed
-
- Amano M, Mukai H, Ono Y, Chihara K, Matsui T, Hamajima Y, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Kaibuchi K. Identification of a putative target for Rho as the serine-threonine kinase protein kinase N. Science. 1996;271:648–650. - PubMed
-
- Amieva M, Furthmayr H. Subcellular localization of moesin in dynamic filopodia, retraction fibers, and other structures involved in substrate exploration, attachment, and cell-cell contacts. Exp Cell Res. 1995;219:180–196. - PubMed
-
- Berryman M, Franck Z, Bretscher A. Ezrin is concentrated in the apical microvilli of a wide variety of epithelial cells whereas moesin is found primarily in endothelial cells. J Cell Sci. 1993;105:1025–1043. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

