Activation of the p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway inhibits Cdc2 activation and entry into M-phase in cycling Xenopus egg extracts
- PMID: 9450967
- PMCID: PMC25274
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.2.451
Activation of the p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway inhibits Cdc2 activation and entry into M-phase in cycling Xenopus egg extracts
Abstract
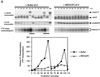
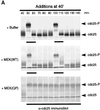
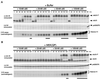
We have added constitutively active MAP kinase/ERK kinase (MEK), an activator of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, to cycling Xenopus egg extracts at various times during the cell cycle. p42MAPK activation during entry into M-phase arrested the cell cycle in metaphase, as has been shown previously. Unexpectedly, p42MAPK activation during interphase inhibited entry into M-phase. In these interphase-arrested extracts, H1 kinase activity remained low, Cdc2 was tyrosine phosphorylated, and nuclei continued to enlarge. The interphase arrest was overcome by recombinant cyclin B. In other experiments, p42MAPK activation by MEK or by Mos inhibited Cdc2 activation by cyclin B. PD098059, a specific inhibitor of MEK, blocked the effects of MEK(QP) and Mos. Mos-induced activation of p42MAPK did not inhibit DNA replication. These results indicate that, in addition to the established role of p42MAPK activation in M-phase arrest, the inappropriate activation of p42MAPK during interphase prevents normal entry into M-phase.
Figures






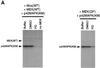

Similar articles
-
Induction of a G2-phase arrest in Xenopus egg extracts by activation of p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase.Mol Biol Cell. 1997 Nov;8(11):2157-69. doi: 10.1091/mbc.8.11.2157. Mol Biol Cell. 1997. PMID: 9362060 Free PMC article.
-
Mos-induced p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation stabilizes M-phase in Xenopus egg extracts after cyclin destruction.Biol Cell. 1998 Nov;90(8):565-72. Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 10069001
-
Requirement for MAPK activation for normal mitotic progression in Xenopus egg extracts.Science. 1998 Nov 13;282(5392):1312-5. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5392.1312. Science. 1998. PMID: 9812894
-
Regulation of the meiotic cell cycle in oocytes.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;12(6):666-75. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00150-2. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11063930 Review.
-
The mitogen activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway: from the cell surface to the nucleus.Cell Signal. 1994 Aug;6(6):581-9. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(94)90041-8. Cell Signal. 1994. PMID: 7857762 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of ERK-MAPK signaling in human epidermis.BMC Syst Biol. 2015 Jul 25;9:41. doi: 10.1186/s12918-015-0187-6. BMC Syst Biol. 2015. PMID: 26209520 Free PMC article.
-
Mathematical Model Explaining the Role of CDC6 in the Diauxic Growth of CDK1 Activity during the M-Phase of the Cell Cycle.Cells. 2019 Nov 28;8(12):1537. doi: 10.3390/cells8121537. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31795221 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic studies of the mitotic activation of Mos.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;26(14):5300-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00273-06. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16809767 Free PMC article.
-
H2S-releasing nanoemulsions: a new formulation to inhibit tumor cells proliferation and improve tissue repair.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):84338-84358. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12609. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27741519 Free PMC article.
-
Mos activates MAP kinase in mouse oocytes through two opposite pathways.EMBO J. 2000 Nov 15;19(22):6065-74. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.22.6065. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 11080153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
-
- Barth H, Hoffmann I, Klein S, Kaszkin M, Richards J, Kinzel V. Role of Cdc25-C phosphatase in the immediate G2 delay induced by the exogenous factors epidermal growth factor and phorbol ester. J Cell Physiol. 1996;168:589–599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

