Biologic bypass with the use of adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of the complementary deoxyribonucleic acid for vascular endothelial growth factor 121 improves myocardial perfusion and function in the ischemic porcine heart
- PMID: 9451061
- PMCID: PMC9464358
- DOI: 10.1016/s0022-5223(98)70455-6
Biologic bypass with the use of adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of the complementary deoxyribonucleic acid for vascular endothelial growth factor 121 improves myocardial perfusion and function in the ischemic porcine heart
Abstract
Objectives: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a potent angiogenic mediator, can be delivered to targeted tissues by means of a replication-deficient adenovirus (Ad) vector. We hypothesized that direct administration of Ad vector expressing the VEGF121 complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (AdGVVEGF121.10) into regions of ischemic myocardium would enhance collateral vessel formation and improve regional perfusion and function.
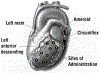
Methods: Yorkshire swine underwent thoracotomy and placement of an Ameroid constrictor (Research Instruments & MFG, Corvallis, Ore.) on the circumflex coronary artery. Three weeks later, myocardial perfusion and function were assessed by single photon emission computed tomography imaging (SPECT) with 99mTc-labeled sestamibi and by echocardiography during rest and stress. AdGVVEGF121.10 (n = 7) or the control vector, AdNull (n = 8), was administered directly into the myocardium at 10 sites in the circumflex distribution (10(8) pfu/site). Four weeks later, these studies were repeated and ex vivo angiography was performed.
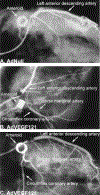
Results: SPECT imaging 4 weeks after vector administration demonstrated significant reduction in the ischemic area at stress in AdGVVEFG121.10-treated animals compared with AdNull control animals (p = 0.005). Stress echocardiography at the same time demonstrated improved segmental wall thickening in AdGVVEGF121.10 animals compared with AdNull control animals (p = 0.03), with AdGVVEGF121.10 animals showing nearly normalized function in the circumflex distribution. Collateral vessel development assessed by angiography was also significantly greater in AdGVVEGF121.10 animals than in AdNull control animals (p = 0.04), with almost complete reconstitution of circumflex filling in AdGVVEGF121.10 animals.
Conclusions: An Ad vector expressing the VEGF121 cDNA induces collateral vessel development in ischemic myocardium and results in significant improvement in both myocardial perfusion and function. Such a strategy may be useful in patients with ischemic heart disease in whom complete revascularization is not possible.
Figures


References
-
- Engler DA. Use of vascular endothelial growth factor for therapeutic angiogenesis. Circulation 1996;94:1496–8. - PubMed
-
- Simons M, Ware JA. Food for starving hearts. Nature Med 1996;2:519–20. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J, Shing Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 1992;267: 10931–4. - PubMed
-
- Schaper W, Ito WD. Molecular mechanisms of coronary collateral vessel growth. Circ Res 1996;79:911–9. - PubMed
-
- Banai S, Jaklitsch MT, Shou M, et al. Angiogenic-induced enhancement of collateral blood flow to ischemic myocardium by vascular endothelial growth factor in dogs. Circulation 1994;89:2183–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

