Anthrax toxin-mediated delivery in vivo and in vitro of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope from ovalbumin
- PMID: 9453617
- PMCID: PMC107948
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.2.615-619.1998
Anthrax toxin-mediated delivery in vivo and in vitro of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope from ovalbumin
Abstract
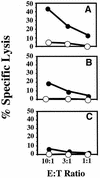
We reported earlier that a nontoxic form of anthrax toxin was capable of delivering a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) epitope in vivo, such that a specific CTL response was primed against the epitope. The epitope, of bacterial origin, was fused to an N-terminal fragment (LFn) from the lethal-factor component of the toxin, and the fusion protein was injected, together with the protective antigen (PA) component, into BALB/c mice. Here we report that PA plus LFn is capable of delivering a different epitope--OVA(257-264) from ovalbumin. Delivery was accomplished in a different mouse haplotype, H-2Kb and occurred in vitro as well as in vivo. An OVA(257-264)-specific CTL clone, GA-4, recognized EL-4 cells treated in vitro with PA plus as little as 30 fmol of the LFn-OVA(257-264) fusion protein. PA mutants attenuated in toxin self-assembly or translocation were inactive, implying that the role of PA in epitope delivery is the same as that in toxin action. Also, we showed that OVA(257-264)-specific CTL could be induced to proliferate by incubation with splenocytes treated with PA plus LFn-OVA(257-264). These findings imply that PA-LFn may serve as a general delivery vehicle for CTL epitopes in vivo and as a safe, efficient tool for the ex vivo expansion of patient-derived CTL for use in adoptive immunotherapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of furin in delivery of a CTL epitope of an anthrax toxin-fusion protein.Microbiol Immunol. 2001;45(2):119-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2001.tb01279.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11293477
-
Anthrax toxin-mediated delivery of a cytotoxic T-cell epitope in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Oct 29;93(22):12531-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.22.12531. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8901616 Free PMC article.
-
Anthrax toxin as a molecular tool for stimulation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes: disulfide-linked epitopes, multiple injections, and role of CD4(+) cells.Infect Immun. 1998 Oct;66(10):4696-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.10.4696-4699.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9746566 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitopes fused to anthrax toxin induce protective antiviral immunity.Infect Immun. 1999 Jul;67(7):3290-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.7.3290-3296.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10377103 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal immunization with CTL epitope peptides from HIV-1 or ovalbumin and the mucosal adjuvant cholera toxin induces peptide-specific CTLs and protection against tumor development in vivo.J Immunol. 1997 Jan 15;158(2):834-41. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 8993001
Cited by
-
Stimulation of CD8+ T cells following diphtheria toxin-mediated antigen delivery into dendritic cells.Infect Immun. 2006 Feb;74(2):1001-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.2.1001-1008.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16428746 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells fail to respond to Shigella flexneri.Infect Immun. 2011 May;79(5):2021-30. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00939-10. Epub 2011 Feb 28. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21357720 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity of anthrax toxin is influenced by receptor expression.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008 Sep;15(9):1330-6. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00103-08. Epub 2008 Jul 2. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18596206 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-mediated uptake of an extracellular Bcl-x(L) fusion protein inhibits apoptosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Aug 17;96(17):9563-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.17.9563. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10449732 Free PMC article.
-
Binary bacterial toxins: biochemistry, biology, and applications of common Clostridium and Bacillus proteins.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004 Sep;68(3):373-402, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.68.3.373-402.2004. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15353562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmed R, Gray D. Immunological memory and protective immunity: understanding their relation. Science. 1996;272:54–60. - PubMed
-
- Arora N, Klimpel K R, Singh Y, Leppla S H. Fusions of anthrax toxin lethal factor to the ADP-ribosylation domain of Pseudomonas exotoxin A are potent cytotoxins which are translocated to the cytosol of mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:15542–15548. - PubMed
-
- Arora N, Leppla S H. Residues 1–254 of anthrax toxin lethal factor are sufficient to cause cellular uptake of fused polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:3334–3341. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

