Fornix lesions can facilitate acquisition of the transverse patterning task: a challenge for "configural" theories of hippocampal function
- PMID: 9454867
- PMCID: PMC6792739
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-04-01622.1998
Fornix lesions can facilitate acquisition of the transverse patterning task: a challenge for "configural" theories of hippocampal function
Abstract
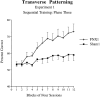
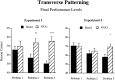
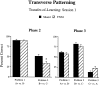
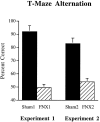
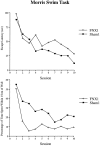
Configural theories of hippocampal function predict that hippocampal dysfunction should impair acquisition of the transverse patterning task, which involves the concurrent solution of three discrimination problems: A+ versus B-; B+ versus C-; and C+ versus A-. The present study tested this prediction in rats using computer-graphic stimuli presented on a touchscreen. Experiment 1 assessed the effects of fornix lesions when the three problems were introduced sequentially (phase 1: A+ vs B-; phase 2: A+ vs B-, B+ vs C-; phase 3: A+ vs B-, B+ vs C-, C+ vs A-). Fornix lesions significantly facilitated acquisition of the complete transverse patterning task (phase 3) but had no effect on the number of sessions or errors required to attain criterion during phase 1 or phase 2. In experiment 2, in which all three problems were presented concurrently from the outset of training, fornix-lesioned animals outperformed control animals during the seventh block of acquisition trials and were not impaired during any stage of acquisition. Importantly, these same animals were significantly impaired on two allocentric spatial tasks: T-maze alternation (experiments 1 and 2) and the Morris Swim Task (experiment 1). These results contradict the predictions of configural theories of hippocampal function and cast doubt on the popular notion that spatial learning is a special case of configural learning.
Figures



References
-
- Aggleton JP, Hunt PR, Rawlins JNP. The effects of hippocampal lesions upon spatial and non-spatial tests of working memory. Behav Brain Res. 1986;19:133–146. - PubMed
-
- Aggleton JP, Keith AB, Rawlins JNP, Hunt PR, Sahgal A. Removal of the hippocampus and transection of the fornix produce comparable deficits on delayed non-matching to position by rats. Behav Brain Res. 1992;52:61–71. - PubMed
-
- Aggleton JP, Hunt PR, Nagle S, Neave N. The effects of selective lesions within the anterior thalamic nuclei on spatial memory in the rat. Behav Brain Res. 1996;81:189–198. - PubMed
-
- Alvarado MC, Rudy JW. A comparison of kainic acid plus colchicine and ibotenic acid-induced hippocampal formation damage on four configural tasks in rats. Behav Neurosci. 1995a;109:1052–1062. - PubMed
-
- Alvarado MC, Rudy JW. Rats with damage to the hippocampal formation are impaired on the transverse-patterning problem but not on elemental discriminations. Behav Neurosci. 1995b;109:204–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
