Detection of immunoglobulin G and A antibodies to rubella virus in urine and antibody responses to vaccine-induced infection
- PMID: 9455874
- PMCID: PMC121385
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.5.1.24-27.1998
Detection of immunoglobulin G and A antibodies to rubella virus in urine and antibody responses to vaccine-induced infection
Abstract
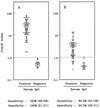
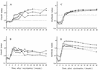
Urine and serum samples from 89 healthy volunteers and three healthy individuals who underwent rubella vaccination were tested for immunoglobulin G (IgG), IgA, and IgM to rubella virus (RV) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay methods. Subjects with positive (n = 68) or negative (n = 21) results for serum IgG were exactly the same as those with the corresponding results for urinary IgG. Both urinary and serum IgG levels remained elevated from the 3rd or 4th week after vaccination until the end of the study. Both urinary IgA and serum IgM levels tended to increase rapidly between the 3rd and 5th week and then gradually decrease until the end of the study, but the levels of both remained positive except for one sample each at the end (26th week). On the other hand, the ratio of anti-RV IgA titer to anti-RV IgG titer in urine (urinary anti-RV IgA/IgG ratio) increased rapidly between the 3rd and 4th week after vaccination and then rapidly returned to the ratio levels of the subjects positive for serum IgG from among the healthy volunteers. In summary, detection of urinary anti-RV IgG should be useful for screening for previous RV infection, and measurement of urinary anti-RV IgA/IgG ratio might be useful for diagnosing recent infection.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Nakib W, Best J M, Banatvala J E. Rubella-specific serum and nasopharyngeal immunoglobulin responses following naturally acquired and vaccine-induced infection. Lancet. 1975;i:182–185. - PubMed
-
- Best J M, Banatvala J E, Watson D. Serum IgM and IgG responses in postnatally acquired rubella. Lancet. 1969;ii:65–68. - PubMed
-
- Burgin-Wolff A, Hernandy R, Just M. Separation of rubella IgM, IgA and IgG antibodies by gel filtration on agarose. Lancet. 1971;ii:1278–1280. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

