Age-stratified seroprevalence of neutralizing antibodies to astrovirus types 1 to 7 in humans in The Netherlands
- PMID: 9455876
- PMCID: PMC121387
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.5.1.33-37.1998
Age-stratified seroprevalence of neutralizing antibodies to astrovirus types 1 to 7 in humans in The Netherlands
Abstract
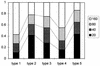
Astroviruses are a new family of positive-stranded RNA viruses that cause gastroenteritis in a wide range of animals and in humans. Seven types of astrovirus, tentatively considered serotypes, have been distinguished by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) or immunoelectron microscopy, but it is unclear whether the serotype designation is used properly. To test human sera for the presence of neutralizing antibodies and to type field strains, neutralization tests (NT) using CaCo2 tissue-culture-adapted astrovirus strains 1 to 7 and the corresponding rabbit reference sera were developed. In rabbits, neutralizing antibodies were predominantly serotype specific, with the exception of low-level cross-reactivity in astrovirus serotype 4 reference serum with astrovirus serotype 1 virus. Similarly, in humans, no evidence of cross-reactivity was found for the serotype combinations tested (all except the combination 1 and 7 and the combination 6 and 7). Typing by NT was concordant with typing by ELISA and genotyping, with one exception. The seroprevalence rates of neutralizing antibodies in an age-stratified sample of the population in Utrecht Province (n = 242) were 91% for astrovirus serotype 1, 69% for astrovirus serotype 3, 56% for astrovirus serotype 4, 36% for astrovirus serotype 5, 31% for astrovirus serotype 2, 16% for astrovirus serotype 6, and 10% for astrovirus serotype 7. Acquisition of antibodies was slower among persons seropositive for astrovirus serotype 5 than among those seropositive for astrovirus serotypes 1 to 4, suggesting that the epidemiology of serotype 5 astrovirus is different from that of astrovirus serotypes 1 to 4.
Figures


References
-
- Echeverria P, Hoge C W, Bodhidatta L, Tungtaem C, Herrmann J, Imlarp S, Tamura K. Etiology of diarrhea in a rural community in western Thailand: importance of enteric viruses and enterovirulent Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1994;169:916–919. - PubMed
-
- Grandien M, Forsgren M, Ehrnst A. Enteroviruses and reoviruses. In: Schmidt N J, Emmons R W, editors. Diagnostic procedures for viral, rickettsial, and chlamydial infections. 6th ed. Washington, D.C: APHA Inc.; 1989. pp. 513–578.
-
- Herrmann J E, Hudson R W, Perron-Henry D M, Kurtz J B, Blacklow N R. Antigenic characterization of cell-cultivated astrovirus serotypes and development of astrovirus-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1988;158:182–185. - PubMed
-
- Hudson R W, Herrmann J E, Blacklow N R. Plaque quantitation and virus neutralization assays for human astroviruses. Arch Virol. 1989;108:33–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

