Caveolin transfection results in caveolae formation but not apical sorting of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins in epithelial cells
- PMID: 9456321
- PMCID: PMC2140173
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.140.3.617
Caveolin transfection results in caveolae formation but not apical sorting of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins in epithelial cells
Abstract
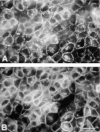
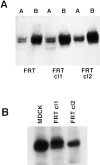
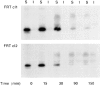
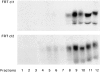
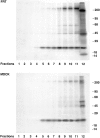
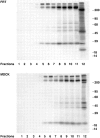
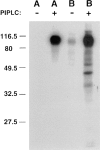
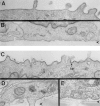
Most epithelial cells sort glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins to the apical surface. The "raft" hypothesis, based on data mainly obtained in the prototype cell line MDCK, postulates that apical sorting depends on the incorporation of apical proteins into cholesterol/glycosphingolipid (GSL) rafts, rich in the cholesterol binding protein caveolin/VIP21, in the Golgi apparatus. Fischer rat thyroid (FRT) cells constitute an ideal model to test this hypothesis, since they missort both endogenous and transfected GPI-anchored proteins to the basolateral plasma membrane and fail to incorporate them into cholesterol/glycosphingolipid clusters. Because FRT cells lack caveolin, a major component of the caveolar coat that has been proposed to have a role in apical sorting of GPI-anchored proteins (Zurzolo, C., W. Van't Hoff, G. van Meer, and E. Rodriguez-Boulan. 1994. EMBO [Eur. Mol. Biol. Organ.] J. 13:42-53.), we carried out experiments to determine whether the lack of caveolin accounted for the sorting/clustering defect of GPI-anchored proteins. We report here that FRT cells lack morphological caveolae, but, upon stable transfection of the caveolin1 gene (cav1), form typical flask-shaped caveolae. However, cav1 expression did not redistribute GPI-anchored proteins to the apical surface, nor promote their inclusion into cholesterol/GSL rafts. Our results demonstrate that the absence of caveolin1 and morphologically identifiable caveolae cannot explain the inability of FRT cells to sort GPI-anchored proteins to the apical domain. Thus, FRT cells may lack additional factors required for apical sorting or for the clustering with GSLs of GPI-anchored proteins, or express factors that inhibit these events. Alternatively, cav1 and caveolae may not be directly involved in these processes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
VIP21/caveolin, glycosphingolipid clusters and the sorting of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins in epithelial cells.EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):42-53. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06233.x. EMBO J. 1994. PMID: 8306971 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosphingolipid clusters and the sorting of GPI-anchored proteins in epithelial cells.Braz J Med Biol Res. 1994 Feb;27(2):317-22. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1994. PMID: 7521706
-
Detergent-insoluble GPI-anchored proteins are apically sorted in fischer rat thyroid cells, but interference with cholesterol or sphingolipids differentially affects detergent insolubility and apical sorting.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Feb;11(2):531-42. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.2.531. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10679012 Free PMC article.
-
Detergent-resistant membrane microdomains and apical sorting of GPI-anchored proteins in polarized epithelial cells.Int J Med Microbiol. 2002 Feb;291(6-7):439-45. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00151. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11890542 Review.
-
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins: Membrane organization and transport.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Apr;1858(4):632-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.12.018. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26706096 Review.
Cited by
-
Unravelling protein sorting.Nat Cell Biol. 2004 Apr;6(4):282-4. doi: 10.1038/ncb0404-282. Nat Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15057238 Free PMC article.
-
Arenavirus entry occurs through a cholesterol-dependent, non-caveolar, clathrin-mediated endocytic mechanism.Virology. 2007 Dec 5;369(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.07.014. Epub 2007 Aug 14. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17698159 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced caveolae density in arteries of SHR contributes to endothelial dysfunction and ROS production.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 30;9(1):6696. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43193-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31040342 Free PMC article.
-
The activity of the epithelial sodium channels is regulated by caveolin-1 via a Nedd4-2-dependent mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 8;284(19):12663-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809737200. Epub 2009 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19304660 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial-specific expression of caveolin-1 impairs microvascular permeability and angiogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jan 4;102(1):204-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406092102. Epub 2004 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15615855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson RGW. Plasmalemmal caveolae and GPI-anchored membrane proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993;5:647–652. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Crise B, Rose JK. Mechanism of membrane anchoring affects polarized expression of two proteins in MDCK cells. Science. 1989;245:1499–1501. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Rose JK. Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipid-enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell. 1992;68:533–544. - PubMed
-
- Cross GAM. Eukaryotic protein modification and membrane attachment via phosphatidylinositol. Cell. 1987;48:179–181. - PubMed

