Immunolocalization of Hsp60 in Legionella pneumophila
- PMID: 9457851
- PMCID: PMC106915
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.3.505-513.1998
Immunolocalization of Hsp60 in Legionella pneumophila
Abstract
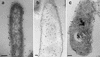
One of the most abundant proteins synthesized by Legionella pneumophila, particularly during growth in a variety of eukaryotic host cells, is Hsp60, a member of the GroEL family of molecular chaperones. The present study was initiated in response to a growing number of reports suggesting that for some bacteria, including L. pneumophila, Hsp60 may exist in extracytoplasmic locations. Immunolocalization techniques with Hsp60-specific monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies were used to define the subcellular location and distribution of Hsp60 in L. pneumophila grown in vitro, or in vivo inside of HeLa cells. For comparative purposes Escherichia coli, expressing recombinant L. pneumophila Hsp60, was employed. In contrast to E. coli, where Hsp60 was localized exclusively in the cytoplasm, in L. pneumophila Hsp60 was predominantly associated with the cell envelope, conforming to a distribution pattern typical of surface molecules that included the major outer membrane protein OmpS and lipopolysaccharide. Interestingly, heat-shocked L. pneumophila organisms exhibited decreased overall levels of cell-associated Hsp60 epitopes and increased relative levels of surface epitopes, suggesting that Hsp60 was released by stressed bacteria. Putative secretion of Hsp60 by L. pneumophila was further indicated by the accumulation of Hsp60 in the endosomal space, between replicating intracellular bacteria. These results are consistent with an extracytoplasmic location for Hsp60 in L. pneumophila and further suggest both the existence of a novel secretion mechanism (not present in E. coli) and a potential role in pathogenesis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Surface-associated hsp60 chaperonin of Legionella pneumophila mediates invasion in a HeLa cell model.Infect Immun. 1998 Oct;66(10):4602-10. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.10.4602-4610.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9746556 Free PMC article.
-
Legionella pneumophila has two 60-kilodalton heat-shock proteins.Curr Microbiol. 1995 Dec;31(6):332-5. doi: 10.1007/BF00294694. Curr Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8528004
-
Elevated levels of Legionella pneumophila stress protein Hsp60 early in infection of human monocytes and L929 cells correlate with virulence.Infect Immun. 1996 Jun;64(6):1968-76. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.6.1968-1976.1996. Infect Immun. 1996. PMID: 8675295 Free PMC article.
-
Surface-associated heat shock proteins of Legionella pneumophila and Helicobacter pylori: roles in pathogenesis and immunity.Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 1999;7(1-2):58-63. doi: 10.1155/S1064744999000125. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 1999. PMID: 10231011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenicity of Legionella pneumophila.Int J Med Microbiol. 2001 Nov;291(5):331-43. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00139. Int J Med Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11727817 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome analysis of cyst formation in Rhodospirillum centenum reveals large global changes in expression during cyst development.BMC Genomics. 2015 Feb 13;16(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1250-9. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25758168 Free PMC article.
-
Surface-associated hsp60 chaperonin of Legionella pneumophila mediates invasion in a HeLa cell model.Infect Immun. 1998 Oct;66(10):4602-10. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.10.4602-4610.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9746556 Free PMC article.
-
Chaperonin 60 unfolds its secrets of cellular communication.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2002 Oct;7(4):317-29. doi: 10.1379/1466-1268(2002)007<0317:cuisoc>2.0.co;2. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2002. PMID: 12653476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The purified and recombinant Legionella pneumophila chaperonin alters mitochondrial trafficking and microfilament organization.Infect Immun. 2009 Nov;77(11):4724-39. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00150-09. Epub 2009 Aug 17. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19687203 Free PMC article.
-
Surface-exposed proteins of Ehrlichia chaffeensis.Infect Immun. 2007 Aug;75(8):3833-41. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00188-07. Epub 2007 May 21. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17517859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu Kwaik Y, Gao L-Y, Harb O S, Stone B J. Transcriptional regulation of the macrophage-induced gene (gspA) of Legionella pneumophila and phenotypic characterization of a null mutant. Mol Microbiol. 1997;24:629–642. - PubMed
-
- Baumann P, Moran N A, Baumann L. The evolution and genetics of aphid endosymbionts. BioScience. 1997;47:12–20.
-
- Berryman M A, Rodewald R D. An enhanced method for post-embedding immunocytochemical staining which preserves cell membranes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990;38:159–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

