Genetic analysis, using P22 challenge phage, of the nitrogen activator protein DNA-binding site in the Klebsiella aerogenes put operon
- PMID: 9457859
- PMCID: PMC106923
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.3.571-577.1998
Genetic analysis, using P22 challenge phage, of the nitrogen activator protein DNA-binding site in the Klebsiella aerogenes put operon
Abstract
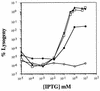
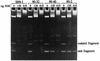
The nac gene product is a LysR regulatory protein required for nitrogen regulation of several operons from Klebsiella aerogenes and Escherichia coli. We used P22 challenge phage carrying the put control region from K. aerogenes to identify the nucleotide residues important for nitrogen assimilation control protein (NAC) binding in vivo. Mutations in an asymmetric 30-bp region prevented DNA binding by NAC. Gel retardation experiments confirmed that NAC specifically binds to this sequence in vitro, but NAC does not bind to the corresponding region from the put operon of Salmonella typhimurium, which is not regulated by NAC.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The nac (nitrogen assimilation control) gene from Klebsiella aerogenes.J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(7):2107-15. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.7.2107-2115.1993. J Bacteriol. 1993. PMID: 8458853 Free PMC article.
-
Alanine catabolism in Klebsiella aerogenes: molecular characterization of the dadAB operon and its regulation by the nitrogen assimilation control protein.J Bacteriol. 1998 Feb;180(3):563-70. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.3.563-570.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9457858 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the Escherichia coli lacZ promoter by the Klebsiella aerogenes nitrogen assimilation control protein (NAC), a LysR family transcription factor.J Bacteriol. 1995 Aug;177(16):4820-4. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.16.4820-4824.1995. J Bacteriol. 1995. PMID: 7642513 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the NAC protein in the nitrogen regulation of Klebsiella aerogenes.Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2575-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01965.x. Mol Microbiol. 1991. PMID: 1664020 Review.
-
A NAC for regulating metabolism: the nitrogen assimilation control protein (NAC) from Klebsiella pneumoniae.J Bacteriol. 2010 Oct;192(19):4801-11. doi: 10.1128/JB.00266-10. Epub 2010 Jul 30. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20675498 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Properties of the NAC (nitrogen assimilation control protein)-binding site within the ureD promoter of Klebsiella pneumoniae.J Bacteriol. 2010 Oct;192(19):4821-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.00883-09. Epub 2010 Jul 9. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20622063 Free PMC article.
-
General nitrogen regulation of nitrate assimilation regulatory gene nasR expression in Klebsiella oxytoca M5al.J Bacteriol. 1999 Dec;181(23):7274-84. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.23.7274-7284.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10572131 Free PMC article.
-
The nac (nitrogen assimilation control) gene from Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 1998 Mar;180(5):1166-73. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.5.1166-1173.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9495755 Free PMC article.
-
The LysR-type nitrogen assimilation control protein forms complexes with both long and short DNA binding sites in the absence of coeffectors.J Bacteriol. 2010 Oct;192(19):4827-33. doi: 10.1128/JB.00968-09. Epub 2010 Apr 2. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20363946 Free PMC article.
-
Expanded role for the nitrogen assimilation control protein in the response of Klebsiella pneumoniae to nitrogen stress.J Bacteriol. 2010 Oct;192(19):4812-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00931-09. Epub 2010 Mar 26. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20348267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bender R A. The role of the NAC protein in the nitrogen regulation of Klebsiella aerogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1991;5:2575–2580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

