Archaeal binding protein-dependent ABC transporter: molecular and biochemical analysis of the trehalose/maltose transport system of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus litoralis
- PMID: 9457875
- PMCID: PMC106939
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.3.680-689.1998
Archaeal binding protein-dependent ABC transporter: molecular and biochemical analysis of the trehalose/maltose transport system of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus litoralis
Abstract
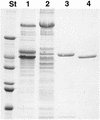
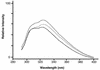
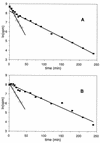
We report the cloning and sequencing of a gene cluster encoding a maltose/trehalose transport system of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus litoralis that is homologous to the malEFG cluster encoding the Escherichia coli maltose transport system. The deduced amino acid sequence of the malE product, the trehalose/maltose-binding protein (TMBP), shows at its N terminus a signal sequence typical for bacterial secreted proteins containing a glyceride lipid modification at the N-terminal cysteine. The T. litoralis malE gene was expressed in E. coli under control of an inducible promoter with and without its natural signal sequence. In addition, in one construct the endogenous signal sequence was replaced by the E. coli MalE signal sequence. The secreted, soluble recombinant protein was analyzed for its binding activity towards trehalose and maltose. The protein bound both sugars at 85 degrees C with a Kd of 0.16 microM. Antibodies raised against the recombinant soluble TMBP recognized the detergent-soluble TMBP isolated from T. litoralis membranes as well as the products from all other DNA constructs expressed in E. coli. Transmembrane segments 1 and 2 as well as the N-terminal portion of the large periplasmic loop of the E. coli MalF protein are missing in the T. litoralis MalF. MalG is homologous throughout the entire sequence, including the six transmembrane segments. The conserved EAA loop is present in both proteins. The strong homology found between the components of this archaeal transport system and the bacterial systems is evidence for the evolutionary conservation of the binding protein-dependent ABC transport systems in these two phylogenetic branches.
Figures






References
-
- Argast M, Boos W. Purification and properties of sn-glycerol 3-phosphate-binding protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979;254:10931–10935. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Smith J A, Seidman J G, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: Greene Publishing Associates; 1987.
-
- Bavoil P, Hofnung M, Nikaido H. Identification of a cytoplasmic membrane-associated component of the maltose transport system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980;255:8366–8369. - PubMed
-
- Bohl E, Boos W. Binding protein-dependent transporters: an answer of mathematics to biology. J Comput Appl Math. 1995;63:11–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

