Fibroblast growth factor 2 control of vascular tone
- PMID: 9461194
- PMCID: PMC3850292
- DOI: 10.1038/nm0298-201
Fibroblast growth factor 2 control of vascular tone
Abstract
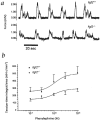
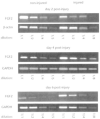
Vascular tone control is essential in blood pressure regulation, shock, ischemia-reperfusion, inflammation, vessel injury/repair, wound healing, temperature regulation, digestion, exercise physiology, and metabolism. Here we show that a well-known growth factor, FGF2, long thought to be involved in many developmental and homeostatic processes, including growth of the tissue layers of vessel walls, functions in vascular tone control. Fgf2 knockout mice are morphologically normal and display decreased vascular smooth muscle contractility, low blood pressure and thrombocytosis. Following intra-arterial mechanical injury, FGF2-deficient vessels undergo a normal hyperplastic response. These results force us to reconsider the function of FGF2 in vascular development and homeostasis in terms of vascular tone control.
Figures
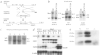

References
-
- Kessler DS, Melton DA. Vertebrate embryonic induction: Mesodermal and neural patterning. Science. 1994;266:596–604. - PubMed
-
- Kimelman D, Kirschner M. Synergistic induction of mesoderm by FGF and TGF-beta and the identification of an mRNA coding for FGF in the early Xenopus embryo. Cell. 1987;51:869–877. - PubMed
-
- Flamme I, Risau W. Induction of vasculogenesis and hematopoiesis in vitro. Development. 1992;116:435–439. - PubMed
-
- Slack JM, Isaacs HV. The Einsteck-method: Position and structure of projections formed by implants of a ventral character. Dev. Biol. 1994;161:313–317. - PubMed
-
- Schneider MD, McLellan WR, Black FM, Parker TG. Growth factors, growth factor response elements, and the cardiac phenotype. Basic Res. Cardiol. 1992;87(Suppl. 2):33–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

