Infection of mice with Mycobacterium bovis-Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) suppresses allergen-induced airway eosinophilia
- PMID: 9463406
- PMCID: PMC2212158
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.4.561
Infection of mice with Mycobacterium bovis-Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) suppresses allergen-induced airway eosinophilia
Abstract
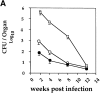
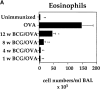
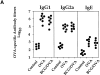
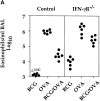
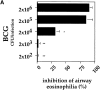
It has been proposed that the increase in prevalence and severity of atopic disorders inversely correlates with exposure to infectious diseases such as tuberculosis. We have investigated this issue by combining an intranasal Mycobacterium bovis-Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) infection with a murine model of allergen, (ovalbumin [OVA]) induced airway eosinophilia. BCG infection either 4 or 12 wk before allergen airway challenge resulted in a 90-95 and 60-70% reduction in eosinophilia within the lungs, respectively, compared to uninfected controls. The inhibition of airway eosinophilia correlated with a reduced level of IL-5 production by T cells from the lymph node draining the site of OVA challenge. Interestingly, BCG infection of the lung had no effect on IgG1 and IgE OVA-specific serum immunoglobulin or blood eosinophil levels. Furthermore, BCG-induced inhibition of airway eosinophilia was strongly reduced in interferon (IFN)-gamma receptor-deficient mice and could be partially reversed by intranasal IL-5 application. Intranasal BCG infections could also reduce the degree of lung eosinophilia and IL-5 produced by T cells after Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection. Taken together, our data suggest that IFN-gamma produced during the T helper cell (Th)1 immune response against BCG suppresses the development of local inflammatory Th2 responses in the lung. Most importantly, this inhibition did not extend to the systemic immunoglobulin response against OVA. Our data support the view that mycobacterial infections have the potential to suppress the development of atopic disorders in humans.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Vaccinations with T-helper type 1 directing adjuvants have different suppressive effects on the development of allergen-induced T-helper type 2 responses.Clin Exp Allergy. 2005 Aug;35(8):1003-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2005.02287.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005. PMID: 16120081
-
Application of heat killed Mycobacterium bovis-BCG into the lung inhibits the development of allergen-induced Th2 responses.Vaccine. 2002 Feb 22;20(11-12):1532-40. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(01)00496-0. Vaccine. 2002. PMID: 11858859
-
Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 suppresses allergen-induced Th2 responses in the airways.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2009;149(3):219-30. doi: 10.1159/000199717. Epub 2009 Feb 12. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19218814
-
Development of an asthma vaccine: research into BCG.Drugs. 2000 Jun;59(6):1217-21. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200059060-00002. Drugs. 2000. PMID: 10882158 Review.
-
Recombinant BCG Expressing IL-12 as A Novel Immunomodulatory Strategy for Allergic Asthma: Opportunities and Challenges.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025 Jun 7;68(1):54. doi: 10.1007/s12016-025-09066-x. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40483388 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of naive CD4+ T-cell responses to an airway antigen during pulmonary mycobacterial infection.Infect Immun. 2007 May;75(5):2260-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01709-06. Epub 2007 Feb 12. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17296758 Free PMC article.
-
Ag85B DNA vaccine suppresses airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma.Respir Res. 2009 Jun 16;10(1):51. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-10-51. Respir Res. 2009. PMID: 19531238 Free PMC article.
-
Flt3-L increases CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ICOS+ cells in the lungs of cockroach-sensitized and -challenged mice.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2010 Mar;42(3):331-40. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0397OC. Epub 2009 May 15. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 19448155 Free PMC article.
-
Viruses and asthma.Allergy. 1998 Oct;53(10):922-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1998.tb03792.x. Allergy. 1998. PMID: 9821471 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Association Between Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Vaccination and Childhood Asthma in the Quebec Birth Cohort on Immunity and Health.Am J Epidemiol. 2017 Aug 1;186(3):344-355. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwx088. Am J Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 28472373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carballido JM, Carballido-Perrig N, Terres G, Heusser CH, Blaser K. Bee venom phospholipase A2-specific T cell clones from human allergic and non-allergic individuals: cytokine patterns change in response to the antigen concentration. Eur J Immunol. 1992;22:1357–1363. - PubMed
-
- Burrows B, Martinez FD, Halonen M, Barbee RA, Cline MG. Association of asthma with serum IgE levels and skin-test reactivity to allergens. N Engl J Med. 1989;320:271–277. - PubMed
-
- Del Prete G. Human Th1 and Th2 lymphocytes: their role in the pathophysiology of atopy. Allergy. 1992;47:450–455. - PubMed
-
- Erb KJ, LeGros G. The role of Th2 type-CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells in asthma. Immunol Cell Biol. 1996;74:206–209. - PubMed
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone: definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986;136:2348–2357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

