Acquisition of Ly49 receptor expression by developing natural killer cells
- PMID: 9463411
- PMCID: PMC2212149
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.4.609
Acquisition of Ly49 receptor expression by developing natural killer cells
Abstract
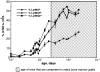
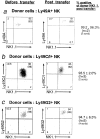
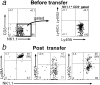
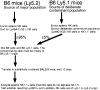
The formation of the repertoire of mouse natural killer (NK) cell receptors for major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules was investigated by determining the developmental pattern of Ly49 receptor expression. During the first days after birth, few or no splenic NK cells express Ly49A, Ly49C, Ly49G2, or Ly49I receptors. The proportion of Ly49+ splenic NK cells gradually rises to adult levels during the first 6-8 wk of life. The appearance of appreciable numbers of splenic Ly49+ NK cells coincides with the appearance of NK activity at 3-4 wk. After in vivo transfer, NK cells not expressing specific Ly49 receptors can give rise to NK cells that do, and cells expressing one of these four Ly49 receptors can give rise to cells expressing others. Once initiated, expression of a Ly49 receptor is stable for at least 10 d after in vivo transfer. Hence, initiation of Ly49 receptor expression occurs successively. Interestingly, expression of one of the receptors tested, Ly49A, did not occur after in vivo transfer of Ly49A- cells. One possible explanation for these data is that the order of Ly49 receptor expression by NK cells is nonrandom. The results provide a framework for evaluating models of NK cell repertoire formation, and how the repertoire is molded by host class I MHC molecules.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MHC class I-Ly49 interactions shape the Ly49 repertoire on murine NK cells.J Immunol. 2001 Jun 1;166(11):6585-92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.11.6585. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11359811
-
NK cells developing in vitro from fetal mouse progenitors express at least one member of the Ly49 family that is acquired in a time-dependent and stochastic manner independently of CD94 and NKG2.Eur J Immunol. 2002 Mar;32(3):868-78. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200203)32:3<868::AID-IMMU868>3.0.CO;2-A. Eur J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11870631
-
Clonal analysis of NK cell development from bone marrow progenitors in vitro: orderly acquisition of receptor gene expression.Eur J Immunol. 2000 Jul;30(7):2074-82. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200007)30:7<2074::AID-IMMU2074>3.0.CO;2-#. Eur J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10940897
-
Specificity, tolerance and developmental regulation of natural killer cells defined by expression of class I-specific Ly49 receptors.Immunol Rev. 1997 Feb;155:41-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1997.tb00938.x. Immunol Rev. 1997. PMID: 9059881 Review.
-
MHC class I recognition by Ly49 natural killer cell receptors.Mol Immunol. 2002 May;38(14):1023-7. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00031-7. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11955594 Review.
Cited by
-
Thymus-dependent modulation of Ly49 inhibitory receptor expression on NK1.1+gamma/delta T cells.Immunology. 2001 Jan;102(1):24-30. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2001.01155.x. Immunology. 2001. PMID: 11168633 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-inflammatory role of natural killer cells in the development of allergic airway disease.Clin Exp Allergy. 2014 Apr;44(4):589-601. doi: 10.1111/cea.12271. Clin Exp Allergy. 2014. PMID: 24397722 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the earliest immune response to in utero hematopoietic cellular transplantation.Chimerism. 2010 Oct;1(2):61-3. doi: 10.4161/chim.1.2.13147. Chimerism. 2010. PMID: 21327049 Free PMC article.
-
Intrahepatic IL-10 maintains NKG2A+Ly49- liver NK cells in a functionally hyporesponsive state.J Immunol. 2010 Mar 1;184(5):2693-701. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901362. Epub 2010 Feb 1. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20124099 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphic residues in HLA-B that mediate HIV control distinctly modulate peptide interactions with both TCR and KIR molecules.Structure. 2024 Aug 8;32(8):1121-1136.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2024.04.015. Epub 2024 May 10. Structure. 2024. PMID: 38733995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ljunggren HG, Kärre K. In search of the ‘missing self ': MHC molecules and NK cell recognition. Immunol Today. 1990;11:237–244. - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama WM, Seaman WE. The Ly-49 and NKR-P1 gene families encoding lectin-like receptors on natural killer cells: the NK gene complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:613–635. - PubMed
-
- Held W, Dorfman JR, Wu M-F, Raulet DH. Major histocompatibility complex class I-dependent skewing of the natural killer cell Ly49 receptor repertoire. Eur J Immunol. 1996;26:2286–2292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

