CD4+ T cell-mediated granulomatous pathology in schistosomiasis is downregulated by a B cell-dependent mechanism requiring Fc receptor signaling
- PMID: 9463412
- PMCID: PMC2212140
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.4.619
CD4+ T cell-mediated granulomatous pathology in schistosomiasis is downregulated by a B cell-dependent mechanism requiring Fc receptor signaling
Abstract
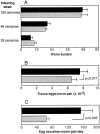
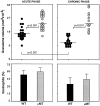
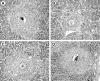
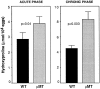
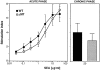
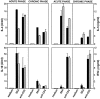
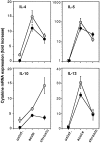
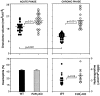
The effector functions of CD4+ T lymphocytes are generally thought to be controlled by distinct populations of regulatory T cells and their soluble products. The role of B cells in the regulation of CD4-dependent host responses is less well understood. Hepatic egg granuloma formation and fibrosis in murine schistosomiasis are dependent on CD4+ lymphocytes, and previous studies have implicated CD8+ T cells or cross-regulatory cytokines produced by T helper (Th) lymphocytes as controlling elements of this pathologic process. In this report, we demonstrate that B cell-deficient (muMT) mice exposed to Schistosoma mansoni develop augmented tissue pathology and, more importantly, fail to undergo the spontaneous downmodulation in disease normally observed during late stages of infection. Unexpectedly, B cell deficiency did not significantly alter T cell proliferative response or cause a shift in the Th1/Th2 balance. Since schistosome-infected Fc receptor-deficient (FcR gamma chain knockout) mice display the same exacerbated egg pathology as that observed in infected muMT mice, the B cell- dependent regulatory mechanism revealed by these experiments appears to require receptor-mediated cell triggering. Together, the data demonstrate that humoral immune response/FcR interactions can play a major role in negatively controlling inflammatory disease induced by CD4+ T cells.
Figures

References
-
- Colley DG, Lewis FA, Todd CW. Adoptive suppression of granuloma formation by T lymphocytes and by cells sensitive to cyclophosphamide. Cell Immunol. 1979;46:192–200. - PubMed
-
- Chensue SW, Wellhausen SR, Boros DL. Modulation of granulomatous hypersensitivity. II. Participation of Lyt1+ and Lyt2+ T lymphocytes in the suppression of granuloma formation and lymphokine production in Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1981;127:363–367. - PubMed
-
- Chensue SW, Warmington KS, Hershey SD, Terebuh PD, Othman M, Kunkel SL. Evolving T cell responses in murine schistosomiasis. Th2 cells mediate secondary granulomatous hypersensitivity and are regulated by CD8+T cells in vivo. J Immunol. 1993;151:1391–1400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

