A cold-adapted lipase of an Alaskan psychrotroph, Pseudomonas sp. strain B11-1: gene cloning and enzyme purification and characterization
- PMID: 9464382
- PMCID: PMC106070
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.64.2.486-491.1998
A cold-adapted lipase of an Alaskan psychrotroph, Pseudomonas sp. strain B11-1: gene cloning and enzyme purification and characterization
Abstract
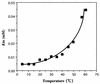
A psychrotrophic bacterium producing a cold-adapted lipase upon growth at low temperatures was isolated from Alaskan soil and identified as a Pseudomonas strain. The lipase gene (lipP) was cloned from the strain and sequenced. The amino acid sequence deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the gene (924 bp) corresponded to a protein of 308 amino acid residues with a molecular weight of 33,714. LipP also has consensus motifs conserved in other cold-adapted lipases, i.e., Lipase 2 from Antarctic Moraxella TA144 (G. Feller, M. Thirty, J. L. Arpigny, and C. Gerday, DNA Cell Biol. 10:381-388, 1991) and the mammalian hormone-sensitive lipase (D. Langin, H. Laurell, L. S. Holst, P. Belfrage, and C. Holm, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:4897-4901, 1993): a pentapeptide, GDSAG, containing the putative active-site serine and an HG dipeptide. LipP was purified from an extract of recombinant Escherichia coli C600 cells harboring a plasmid coding for the lipP gene. The enzyme showed a 1,3-positional specificity toward triolein. p-Nitrophenyl esters of fatty acids with short to medium chains (C4 and C6) served as good substrates. The enzyme was stable between pH 6 and 9, and the optimal pH for the enzymatic hydrolysis of tributyrin was around 8. The activation energies for the hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl butyrate and p-nitrophenyl laurate were determined to be 11.2 and 7.7 kcal/mol, respectively, in the temperature range 5 to 35 degrees C. The enzyme was unstable at temperatures higher than 45 degrees C. The Km of the enzyme for p-nitrophenyl butyrate increased with increases in the assay temperature. The enzyme was strongly inhibited by Zn2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, and Hg2+ but was not affected by phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride and bisnitrophenyl phosphate. Various water-miscible organic solvents, such as methanol and dimethyl sulfoxide, at concentrations of 0 to 30% (vol/vol) activated the enzyme.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cloning and expression of lipP, a gene encoding a cold-adapted lipase from Moritella sp.2-5-10-1.Curr Microbiol. 2008 Feb;56(2):194-8. doi: 10.1007/s00284-007-9051-2. Epub 2007 Nov 1. Curr Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 17973159
-
Molecular cloning and expression of a cold-adapted lipase gene from an Antarctic deep sea psychrotrophic bacterium Pseudomonas sp. 7323.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2008 Sep-Oct;10(5):612-21. doi: 10.1007/s10126-008-9099-4. Epub 2008 May 7. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2008. PMID: 18461394
-
Cloning, heterologous expression, renaturation, and characterization of a cold-adapted esterase with unique primary structure from a psychrotroph Pseudomonas sp. strain B11-1.Protein Expr Purif. 2003 Aug;30(2):171-8. doi: 10.1016/s1046-5928(03)00128-1. Protein Expr Purif. 2003. PMID: 12880765
-
Cloning, expression, and characterization of a cold-adapted lipase gene from an antarctic deep-sea psychrotrophic bacterium, Psychrobacter sp 7195.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 Apr;17(4):604-10. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 18051271
-
Low-temperature lipase from psychrotrophic Pseudomonas sp. strain KB700A.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001 Sep;67(9):4064-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.9.4064-4069.2001. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11526006 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cloning and expression of lipP, a gene encoding a cold-adapted lipase from Moritella sp.2-5-10-1.Curr Microbiol. 2008 Feb;56(2):194-8. doi: 10.1007/s00284-007-9051-2. Epub 2007 Nov 1. Curr Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 17973159
-
Production of alkaline lipase by Corynebacterium paurometabolum, MTCC 6841 isolated from Lake Naukuchiatal, Uttaranchal State, India.Curr Microbiol. 2006 May;52(5):354-8. doi: 10.1007/s00284-005-0224-6. Epub 2006 Apr 6. Curr Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16604420
-
Expression and characterization of a novel heterologous moderately thermostable lipase derived from metagenomics in Streptomyces lividans.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Sep;37(9):883-91. doi: 10.1007/s10295-010-0735-4. Epub 2010 May 21. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20495942
-
Molecular cloning and expression of a cold-adapted lipase gene from an Antarctic deep sea psychrotrophic bacterium Pseudomonas sp. 7323.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2008 Sep-Oct;10(5):612-21. doi: 10.1007/s10126-008-9099-4. Epub 2008 May 7. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2008. PMID: 18461394
-
Purification and biochemical characterization of a cold-active lipase from Antarctic sea ice bacteria Pseudoalteromonas sp. NJ 70.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Sep;39(9):9233-8. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1796-4. Epub 2012 Jun 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22714922
References
-
- Arpigny J L, Feller G, Gerday C. Cloning, sequence and structural features of a lipase from the Antarctic facultative psychrophile Psychrobacter immobilis B10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993;1171:331–333. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Breuil C, Kushner D J. Partial purification and characterization of the lipase of a facultative psychrophilic bacterium (Acinetobacter O16) Can J Microbiol. 1975;21:434–441. - PubMed
-
- Brockerhoff H, Jensen R G, editors. Lipolytic enzymes. New York, N.Y: Academic Press; 1974. pp. 1–3.
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

