Molecular characterization and heterologous expression of the gene encoding a low-molecular-mass endoglucanase from Trichoderma reesei QM9414
- PMID: 9464393
- PMCID: PMC106082
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.64.2.555-563.1998
Molecular characterization and heterologous expression of the gene encoding a low-molecular-mass endoglucanase from Trichoderma reesei QM9414
Abstract
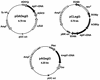
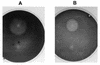
We have isolated the genomic and cDNA clones encoding EG III (a low-molecular-mass endo-beta-1,4-glucanase) gene from Trichoderma reesei QM9414. The nucleotide sequence of the cDNA fragment was verified to contain a 702-bp open reading frame that encodes a 234-amino-acid propeptide. The deduced protein sequence has significant homologies with family H endo-beta-1,4-glucanases. The 16-amino-acid N-terminal sequence was shown to function as a leader peptide for possible secretion. Northern blot analysis showed that the EG III gene transcript, with a length of about 700 bp, was expressed markedly by cellulose but not by glucose. The protein has been expressed as a mature form in Escherichia coli and as secreted forms in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe under the control of tac, alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH1), and human cytomegalovirus promoters, respectively. The S. cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe recombinant strains showed strong cellulolytic activities on agar plates containing carboxymethyl cellulose. The E. coli strain expressed small amounts of EG III in an active form and large amounts of EG III in an inactive form. The molecular masses of the recombinant EG IIIs were estimated to be 25, 28, and 29 kDa for E. coli, S. cerevisiae, and Schizosaccharomyces pombe, respectively, by immunoblot analysis following sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacryl-amide gel electrophoresis. Parts of the yeast recombinant EG IIIs decreased their molecular masses to 25 kDa after treatment with endoglycosidase H and alpha-mannosidase, suggesting that they are N glycosylated at least partly.
Figures






References
-
- Beldman G, Leeuwen M F S-V, Rombouts F M, Voragen F G J. The cellulase of Trichoderma viride. Eur J Biochem. 1985;146:301–308. - PubMed
-
- Claeyssens M, Tomme P. Structure-function relationships of cellulolytic proteins from Trichoderma reesei. In: Kubicek C P, Eveleigh D E, Esterbauer H, Steiner W, Kubicek-Prnz E M, editors. Trichoderma reesei cellulases: biochemistry, genetics, physiology and application. Cambridge, United Kingdom: The Royal Society of Chemistry; 1990. pp. 1–11.
-
- Farkas V, Liskova M, Biely P. Novel media for detection of microbial producers of cellulase and xylanase. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1985;28:137–140.
-
- Giga-Hama Y, Tohda H, Okada H, Owada M K, Okayama H, Kumagai H. High-level expression of human lipocortin I in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe using a novel expression vector. Bio/Technology. 1994;12:400–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

