Reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibition of PCR at low concentrations of template and its implications for quantitative RT-PCR
- PMID: 9464406
- PMCID: PMC106100
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.64.2.669-677.1998
Reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibition of PCR at low concentrations of template and its implications for quantitative RT-PCR
Abstract
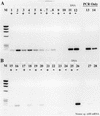
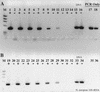
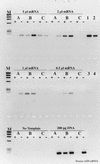
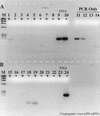
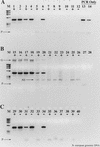
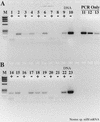
Numerous instances of reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibition of the PCR were observed while developing nonquantitative uncoupled RT-PCR techniques for detecting nitrogenase and ammonia monooxygenase gene expression in situ. The inhibitory effect of RT on the PCR was removed with increasing template concentrations beyond 10(5) to 10(6) copies. Including T4 gene 32 protein during the reverse transcription phase of the RT-PCR reaction increased the RT-PCR product yield by as much as 483%; if gene 32 protein was introduced after reverse transcription but prior to the PCR phase, no improvement in product yield was observed. Addition of 1 microgram of exogenous calf thymus DNA or yeast tRNA did little to relieve RT inhibition of the PCR on both genomic DNA and mRNA templates. These results suggest that RT inhibition of the PCR is mediated through direct interaction with the specific primer-template combination (DNA and RNA) and point to specific assay modifications for estimating the extent of RT inhibition and counteracting some of the inhibitory effect. Furthermore, the working hypothesis of RT inhibition below a 10(5) to 10(6) copy threshold has important implications for quantitative RT-PCR studies. In particular, competitive, quantitative RT-PCR systems will consistently underestimate the actual RNA concentration. Hence, enumerations of RNA templates below 10(5) to 10(6) copies will be relative to an internal standard and will not be an absolute measure of RNA abundance in situ.
Figures

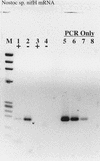
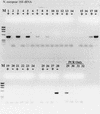
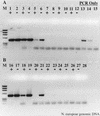
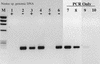
Similar articles
-
Increased yield of PCR products by addition of T4 gene 32 protein to the SMART PCR cDNA synthesis system.Biotechniques. 2001 Jul;31(1):81-3, 86. doi: 10.2144/01311st04. Biotechniques. 2001. PMID: 11464524
-
[Use of the real-time RT-PCR method for investigation of small stable RNA expression level in human epidermoid carcinoma cells A431].Tsitologiia. 2003;45(4):392-402. Tsitologiia. 2003. PMID: 14520871 Russian.
-
Elimination of background signals in a modified polymerase chain reaction-based reverse transcriptase assay.J Virol Methods. 1997 Jul;66(2):247-61. doi: 10.1016/s0166-0934(97)00067-0. J Virol Methods. 1997. PMID: 9255736
-
Strand transfer events during HIV-1 reverse transcription.Virus Res. 2008 Jun;134(1-2):19-38. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.12.017. Epub 2008 Feb 14. Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 18279992 Review.
-
Quantitative analysis of gene expression by ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography.J Chromatogr A. 1998 May 8;806(1):47-60. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(97)00514-1. J Chromatogr A. 1998. PMID: 9639880 Review.
Cited by
-
Shape based kinetic outlier detection in real-time PCR.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Apr 12;11:186. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-186. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20385019 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of internal controls for extraction and amplification of nucleic acids from enteric viruses in water samples.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Jul;77(13):4336-43. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00077-11. Epub 2011 May 20. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21602369 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of immunoglobulin G in blood as a major inhibitor of diagnostic PCR.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Jan;38(1):345-50. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.1.345-350.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10618113 Free PMC article.
-
Organization and differential regulation of a cluster of lignin peroxidase genes of Phanerochaete chrysosporium.J Bacteriol. 1999 Jun;181(11):3427-32. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.11.3427-3432.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10348854 Free PMC article.
-
Application of an RNA amplification method for reliable single-cell transcriptome analysis.Biotechniques. 2015 Sep 1;59(3):137-48. doi: 10.2144/000114331. eCollection 2015 Sep. Biotechniques. 2015. PMID: 26345506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aatsinki J T, Lakkakorpi J T, Pietila E M, Rajaniemi H J. A coupled one-step reverse transcription PCR procedure for generation of full-length open reading frames. BioTechniques. 1994;16:282–288. - PubMed
-
- Alberts B, Sternglanz R. Recent excitement in the DNA replication problem. Nature. 1977;269:655–661. - PubMed
-
- Becker-André M. Absolute levels of mRNA by polymerase chain reaction-aided transcript titration assay. Methods Enzymol. 1993;218:420–445. - PubMed
-
- Becker-André M. Evaluation of absolute mRNA levels by polymerase chain reaction-aided transcript titration assay (PATTY) In: Larrick J W, Siebert P D, editors. Reverse transcriptase PCR. New York, N.Y: Ellis Horwood; 1995. pp. 121–149.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

