Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 subgroups of mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression in endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures
- PMID: 9464988
- PMCID: PMC6792636
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-05-01633.1998
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 subgroups of mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression in endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures
Abstract
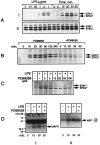
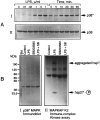
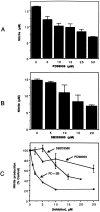
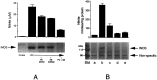
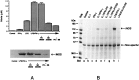
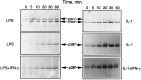
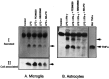
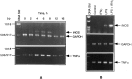
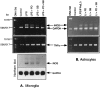
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha) and nitric oxide (NO), the product of inducible NO synthase (iNOS), mediate inflammatory and immune responses in the CNS under a variety of neuropathological situations. They are produced mainly by "activated" astrocytes and microglia, the two immune regulatory cells of the CNS. In this study we have examined the regulation of TNFalpha and iNOS gene expression in endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures, focusing on the role of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascades. The bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was able to activate extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and p38 kinase subgroups of MAP kinases in microglia and astrocytes. ERK activation was sensitive to PD98059, the kinase inhibitor that is specific for ERK kinase. The activity of p38 kinase was inhibited by SB203580, a member of the novel class of cytokine suppressive anti-inflammatory drugs (CSAIDs), as revealed by blocked activation of the downstream kinase, MAP kinase-activated protein kinase-2. The treatment of glial cells with either LPS alone (microglia) or a combination of LPS and interferon-gamma (astrocytes) resulted in an induced production of NO and TNFalpha. The two kinase inhibitors, at micromolar concentrations, individually suppressed and, in combination, almost completely blocked glial production of NO and the expression of iNOS and TNFalpha, as determined by Western blot analysis. Reverse transcriptase-PCR analysis showed changes in iNOS mRNA levels that paralleled iNOS protein and NO while indicating a lack of effect of either of the kinase inhibitors on TNFalpha mRNA expression. The results demonstrate key roles for ERK and p38 MAP kinase cascades in the transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of iNOS and TNFalpha gene expression in endotoxin-activated glial cells.
Figures
References
-
- Adamson DC, Wildemann B, Sasaki M, Glass JD, McArthur JC, Christov VI, Dawson TD, Dawson VL. Immunologic nitric oxide synthase: elevation in severe AIDS dementia and induction by HIV-1 gp41. Science. 1996;274:1917–1921. - PubMed
-
- Badger AM, Bradbeer JN, Votta B, Lee JC, Adams JL, Griswold DE. Pharmacological profile of SB 203580, a selective inhibitor of cytokine suppressive binding protein/p38 kinase, in animal models of arthritis, bone resorption, endotoxin shock, and immune function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;279:1453–1461. - PubMed
-
- Benveniste EN. Role of cytokines in multiple sclerosis, autoimmune encephalitis, and other neurological disorders. In: Aggarwal B, Puri R, editors. Human cytokines: their role in research and therapy. Blackwell Scientific; Boston: 1995. p. 195.
-
- Beutler B. Regulation of cachectin biosynthesis occurs at multiple levels. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;349:229–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
