Role of the Jun kinase pathway in the regulation of c-Jun expression and apoptosis in sympathetic neurons
- PMID: 9464996
- PMCID: PMC6792616
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-05-01713.1998
Role of the Jun kinase pathway in the regulation of c-Jun expression and apoptosis in sympathetic neurons
Abstract
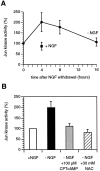
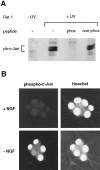
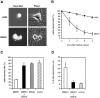
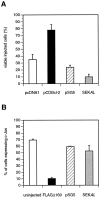
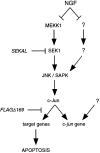
When deprived of nerve growth factor (NGF), developing sympathetic neurons die by apoptosis. This death is associated with an increase in the level of c-Jun protein and is blocked by expression of a c-Jun dominant negative mutant. Here we have investigated whether NGF withdrawal activates Jun kinases, a family of stress-activated protein kinases that can stimulate the transcriptional activity of c-Jun by phosphorylating serines 63 and 73 in the transactivation domain and which can activate c-jun gene expression. We found that sympathetic neurons contained high basal levels of Jun kinase activity that increased further after NGF deprivation. In contrast, p38 kinase, another stress-activated protein kinase that can also stimulate c-jun gene expression, was not activated after NGF withdrawal. Consistent with Jun kinase activation, we found using a phospho-c-Jun-specific antibody that c-Jun was phosphorylated on serine 63 after NGF withdrawal. Furthermore, expression of a constitutively active form of MEK kinase 1 (MEKK1), which strongly activates the Jun kinase pathway, increased c-Jun protein levels and c-Jun phosphorylation and induced apoptosis in the presence of NGF. This death could be prevented by co-expression of SEKAL, a dominant negative mutant of SAPK/ERK kinase 1 (SEK1), an activator of Jun kinase that is a target of MEKK1. In contrast, expression of SEKAL alone did not prevent c-Jun expression, increases in c-Jun phosphorylation, or cell death after NGF withdrawal. Thus, activation of Jun kinase and increases in c-Jun phosphorylation and c-Jun protein levels occur at the same time after NGF withdrawal, but c-Jun levels and phosphorylation are regulated by an SEK1-independent pathway.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Direct inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in sympathetic neurones prevents c-jun promoter activation and NGF withdrawal-induced death.J Neurochem. 2001 Mar;76(5):1439-54. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00150.x. J Neurochem. 2001. PMID: 11238729
-
Comparison between the timing of JNK activation, c-Jun phosphorylation, and onset of death commitment in sympathetic neurones.J Neurochem. 1997 Aug;69(2):550-61. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.69020550.x. J Neurochem. 1997. PMID: 9231712
-
Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis.Science. 1995 Nov 24;270(5240):1326-31. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5240.1326. Science. 1995. PMID: 7481820
-
Stimulation of the stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase subfamilies in perfused heart. p38/RK mitogen-activated protein kinases and c-Jun N-terminal kinases are activated by ischemia/reperfusion.Circ Res. 1996 Aug;79(2):162-73. doi: 10.1161/01.res.79.2.162. Circ Res. 1996. PMID: 8755992 Review.
-
Role of Jun and Jun kinase in resistance of cancer cells to therapy.Drug Resist Updat. 2003 Jun;6(3):147-56. doi: 10.1016/s1368-7646(03)00043-8. Drug Resist Updat. 2003. PMID: 12860462 Review.
Cited by
-
Intracochlear electrical stimulation suppresses apoptotic signaling in rat spiral ganglion neurons after deafening in vivo.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013 Nov;149(5):745-52. doi: 10.1177/0194599813498702. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013. PMID: 23907267 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Gi proteins participate in nerve growth factor-induced activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinases in PC12 cells.Neurochem Res. 2009 Jun;34(6):1101-12. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9880-9. Epub 2008 Nov 14. Neurochem Res. 2009. PMID: 19009346
-
The p75 neurotrophin receptor augments survival signaling in the striatum of pre-symptomatic Q175(WT/HD) mice.Neuroscience. 2016 Jun 2;324:297-306. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.02.069. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 26947127 Free PMC article.
-
Role of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase in regulation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and apoptosis in sympathetic neurons.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Jan;20(1):196-204. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.1.196-204.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10594022 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociation of JNK Activation from Elevated Levels of Reactive Oxygen Species, Cytochrome c Release, and Cell Death in NGF-Deprived Sympathetic Neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jan;55(1):382-389. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0332-2. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 27957682
References
-
- Angel P, Hattori K, Smeal T, Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP1. Cell. 1988;55:875–885. - PubMed
-
- Coso OA, Chiariello M, Yu J-C, Teramoto H, Crespo P, Xu N, Miki T, Gutkind JS. The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell. 1995;81:1137–1146. - PubMed
-
- Dérijard B, Raingeaud J, Barrett T, Wu I-H, Han J, Ulevitch RJ, Davis RJ. Independent human MAP kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science. 1995;267:682–685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
