Turnover of amyloid beta-protein in mouse brain and acute reduction of its level by phorbol ester
- PMID: 9464999
- PMCID: PMC6792617
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-05-01743.1998
Turnover of amyloid beta-protein in mouse brain and acute reduction of its level by phorbol ester
Abstract
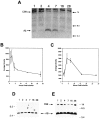
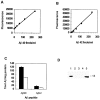
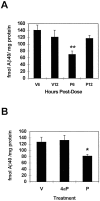
Fibrillar amyloid deposits are defining pathological lesions in Alzheimer's disease brain and are thought to mediate neuronal death. Amyloid is composed primarily of a 39-42 amino acid protein fragment of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), called amyloid beta-protein (Abeta). Because deposition of fibrillar amyloid in vitro has been shown to be highly dependent on Abeta concentration, reducing the proteolytic release of Abeta is an attractive, potentially therapeutic target. Here, the turnover rate of brain Abeta has been determined to define treatment intervals over which a change in steady-state concentration of Abeta could be measured. Mice producing elevated levels of human Abeta were used to determine approximate turnover rates for Abeta and two of its precursors, C99 and APP. The t1/2 for brain Abeta was between 1.0 and 2.5 hr, whereas for C99, immature, and fully glycosylated forms of APP695 the approximate t1/2 values were 3, 3, and 7 hr, respectively. Given the rapid Abeta turnover rate, acute studies were designed using phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), which had been demonstrated previously to reduce Abeta secretion from cells in vitro via induction of protein kinase C (PKC) activity. Six hours after intracortical injection of PMA, Abeta levels were significantly reduced, as measured by both Abeta40- and Abeta42-selective ELISAs, returning to normal by 12 hr. An inactive structural analog of PMA, 4alpha-PMA, had no effect on brain Abeta levels. Among the secreted N-terminal APP fragments, APPbeta levels were significantly reduced by PMA treatment, whereas APPalpha levels were unchanged, in contrast to most cell culture studies. These results indicate that Abeta is rapidly turned over under normal conditions and support the therapeutic potential of elevating PKC activity for reduction of brain Abeta.
Figures



References
-
- Baranyi A, Szente MB, Woody CD. Intracellular injection of phorbol ester increases the excitability of neurons of the motor cortex of awake cats. Brain Res. 1987;424:396–401. - PubMed
-
- Cai XD, Golde TE, Younkin SG. Release of excess amyloid β protein from a mutant amyloid β protein precursor. Science. 1993;259:514–516. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
