Activation of serotonergic neurons in the raphe magnus is not necessary for morphine analgesia
- PMID: 9465010
- PMCID: PMC6792633
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-05-01860.1998
Activation of serotonergic neurons in the raphe magnus is not necessary for morphine analgesia
Abstract
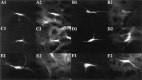
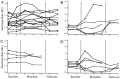
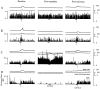
A wealth of pharmacological and behavioral data suggests that spinally projecting serotonergic cells mediate opioid analgesia. A population of medullary neurons, located within raphe magnus (RM) and the neighboring reticular nuclei, contains serotonin and is the source of serotonin in the spinal dorsal horn. To test whether serotonergic neurons mediate opioid analgesia, morphine was administered during recordings from medullary cells that were physiologically characterized as serotonergic (5HTp) by their slow and steady discharge pattern in the lightly anesthetized rat. Selected 5HTp cells (n = 14) were intracellularly labeled, and all contained serotonin immunoreactivity. The discharge of most 5HTp cells was not affected by an analgesic dose of systemic morphine. In a minority of cases, 5HTp cells either increased or decreased their discharge after morphine administration. However, morphine altered the discharge of some 5HTp cells in the absence of producing analgesia and conversely did not alter the discharge of most 5HTp cells in cases in which analgesia occurred. RM cells with irregular discharge patterns and excitatory or inhibitory responses to noxious tail heat were classified as ON and OFF cells, respectively. All ON and OFF cells that were intracellularly labeled (n = 9) lacked serotonin immunoreactivity. All ON cells were inhibited, and most OFF cells were excited by systemic morphine. Because 5HTp cells do not consistently change their discharge during morphine analgesia, they are unlikely to mediate the analgesic effects of morphine. Instead, nonserotonergic cells are likely to mediate morphine analgesia in the anesthetized rat. In light of the sensitivity of morphine analgesia to manipulations of serotonin, serotonin release, although neither necessary nor sufficient for opioid analgesia, is proposed to facilitate the analgesic effects of nonserotonergic RM terminals in the spinal cord.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Physiological identification of pontomedullary serotonergic neurons in the rat.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Mar;77(3):1087-98. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.77.3.1087. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9084584
-
Activity of murine raphe magnus cells predicts tachypnea and on-going nociceptive responsiveness.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Dec;98(6):3121-33. doi: 10.1152/jn.00904.2007. Epub 2007 Oct 3. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17913977 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide FF receptors control morphine-induced analgesia in the parafascicular nucleus and the dorsal raphe nucleus.Eur J Pharmacol. 1997 Jul 9;330(2-3):129-37. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(97)01017-0. Eur J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9253945
-
[Involvement of serotoninergic systems in analgesia induced by electrical stimulation of brain stem areas (author's transl)].J Physiol (Paris). 1981;77(2-3):473-82. J Physiol (Paris). 1981. PMID: 7026772 Review. French.
-
[Relationship between neurons in the nucleus raphe magnus and motor reflex evoked by noxious stimulation].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 1990;15(3):173-6. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 1990. PMID: 2125873 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Review of overlap between thermoregulation and pain modulation in fibromyalgia.Clin J Pain. 2014 Jun;30(6):544-55. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e3182a0e383. Clin J Pain. 2014. PMID: 23887348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cold Case of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 6: Unjust Detention in the Retina?Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(2):120-125. doi: 10.2174/1570159X17666191001141849. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31573889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactive Mechanisms of Supraspinal Sites of Opioid Analgesic Action: A Festschrift to Dr. Gavril W. Pasternak.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Jul;41(5):863-897. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00961-9. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 32970288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opioid microinjection into raphe magnus modulates cardiorespiratory function in mice and rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009 Nov;297(5):R1400-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00140.2009. Epub 2009 Aug 26. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19710394 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiology of nitrous oxide-induced antinociceptive effects.Mol Neurobiol. 2002 Apr;25(2):167-89. doi: 10.1385/MN:25:2:167. Mol Neurobiol. 2002. PMID: 11936558 Review.
References
-
- Alhaider AA, Wilcox GL. Differential roles of 5hydroxytryptamine1A and 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor subtypes in modulating spinal nociceptive transmission in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:378–385. - PubMed
-
- Auerbach S, Fornal C, Jacobs BL. Response of serotonin-containing neurons in nucleus raphe magnus to morphine, noxious stimuli, and periaqueductal gray stimulation in freely moving cats. Exp Neurol. 1985;88:609–628. - PubMed
-
- Barbaro NM, Hammond DL, Fields HL. Effects of intrathecally administered methysergide and yohimbine on microstimulation-produced antinociception in the rat. Brain Res. 1985;343:223–229. - PubMed
-
- Barbaro NM, Heinricher MM, Fields HL. Putative pain modulating neurons in the rostral ventral medulla: reflex-related activity predicts effects of morphine. Brain Res. 1986;366:203–210. - PubMed
-
- Belcher G, Ryall RW, Schaffner R. The differential effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline and raphe stimulation on nociceptive and non-nociceptive dorsal horn interneurones in the cat. Brain Res. 1978;151:307–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
