Genes in the pX region of human T cell leukemia virus I influence Vav phosphorylation in T cells
- PMID: 9465094
- PMCID: PMC19190
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.4.1782
Genes in the pX region of human T cell leukemia virus I influence Vav phosphorylation in T cells
Abstract
Human T cell leukemia virus I (HTLV-I) causes acute leukemic disease in a low percentage of infected individuals through obscure mechanisms. Our studies compare two rabbit HTLV-I-infected T cell lines: one, RH/K34, causes lethal experimental leukemia and the other, RH/K30, mediates asymptomatic infection. We show herein that the product of the protooncogene vav is constitutively Tyr-phosphorylated in RH/K34 but not in RH/K30. A role for the retrovirus in phosphorylation of Vav was assigned by transfection experiments with molecular clones of HTLV-I derived from the two lines. The HTLV-I molecular clone from RH/K30, but not that from RH/K34, down-regulates Vav phosphorylation in a Herpesvirus ateles-transformed T cell line. Use of recombinant virus clones revealed that a pX region sequence differing by two nucleotides between the two clones mediates this down-regulation. Because Vav is involved in T cell signaling and Vav phosphorylation occurs upon activation of T cells, control of the activation state of Vav by viral proteins may relate to the leukemogenic potential of certain HTLV-I-infected cells.
Figures
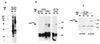



References
-
- Cann A J, Chen I S Y. In: Virology. Fields B N, editor. New York: Raven; 1990. pp. 1520–1527.
-
- de Thé G, Bomford R. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993;9:381–386. - PubMed
-
- Sawasdikosol S, Kindt T J. In: AIDS Research Review. Koff W, Wong-Staal F, Kennedy R C, editors. Vol. 2. New York: Mercel Dekker; 1992. pp. 211–233.
-
- Seto A, Kawanishi M, Matsuda S, Ogawa K, Eguchi T, Miyoshi I. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1987;78:1150. - PubMed
-
- Simpson M R, Leno M, Hubbard B S, Kindt T J. J Infect Dis. 1996;173:722–726. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

