Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and DHEA-sulfate (DHEAS) protect hippocampal neurons against excitatory amino acid-induced neurotoxicity
- PMID: 9465106
- PMCID: PMC19202
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.4.1852
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and DHEA-sulfate (DHEAS) protect hippocampal neurons against excitatory amino acid-induced neurotoxicity
Abstract
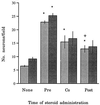
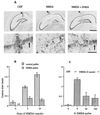
DHEA, together with DHEAS, is the most abundant steroid in the blood of young adult humans. Levels in humans decline with age and during certain types of illness or stress. We have found that DHEA(S) can prevent or reduce the neurotoxic actions in the hippocampus of the glutamate agonists N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) both in vitro and in vivo or alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) and kainic acid in vitro. Pre-treatment with DHEA (10-100 nM for 6-8 h) protected primary hippocampal cultures from embryonic day 18 (E18) embryos against NMDA-induced toxicity (0.1, 1, 10, and 50 mM). DHEA added either with NMDA (1 mM) or 1 h later had lesser, but still significant, protective actions. DHEAS also reduced NMDA-induced toxicity (1 mM), although the lowest effective dose of DHEAS (100 nM) was higher than that of DHEA (10 nM). DHEA (100 nM) protected cultured neurons against the neurotoxic actions of either AMPA (25 microM) or kainic acid (1 mM) as well. In vivo, s.c. pellets of DHEA, which resulted in plasma levels that resembled those in young adult humans, protected hippocampal CA1/2 neurons against unilateral infusions of 5 or 10 nmol of NMDA. Because the release of glutamate has been implicated in the neural damage after cerebral ischemia and other neural insults, these results suggest that decreased DHEA levels may contribute significantly to the increased vulnerability of the aging or stressed human brain to such damage.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bombycis corpus extract (BCE) protects hippocampal neurons against excitatory amino acid-induced neurotoxicity.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2003 May;25(2):191-201. doi: 10.1081/iph-120020469. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2003. PMID: 12784912
-
beta-estradiol, dehydroepiandrosterone, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate protect against N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neurotoxicity in rat hippocampal neurons by different mechanisms.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Oct;311(1):237-45. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.067629. Epub 2004 Jun 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004. PMID: 15175425
-
Non-NMDA antagonists protect against kainate more than AMPA toxicity in the rat hippocampus.Neurosci Lett. 1991 Dec 9;133(2):287-90. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90590-p. Neurosci Lett. 1991. PMID: 1816508
-
Neurobiological and neuropsychiatric effects of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and DHEA sulfate (DHEAS).Front Neuroendocrinol. 2009 Jan;30(1):65-91. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2008.11.002. Epub 2008 Dec 3. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19063914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical development of neurosteroids as neuroprotective agents for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2001;46:379-97. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(01)46069-7. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2001. PMID: 11599307 Review.
Cited by
-
Administration of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) increases serum levels of androgens and estrogens but does not enhance short-term memory in post-menopausal women.Brain Res. 2012 Nov 5;1483:54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.09.015. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22985672 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid dehydroepiandrosterone levels are correlated with brain dehydroepiandrosterone levels, elevated in Alzheimer's disease, and related to neuropathological disease stage.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Aug;93(8):3173-8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-1229. Epub 2008 May 13. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008. PMID: 18477662 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 Negatively Regulates Hippocampus-Dependent Memory Formation through Inhibition of Integrin Signaling and Galectin-3 Phosphorylation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Jul 11;10:217. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00217. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28744198 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic treatment with glucocorticoids alters rat hippocampal and prefrontal cortical morphology in parallel with endogenous agmatine and arginine decarboxylase levels.J Neurochem. 2007 Dec;103(5):1811-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04867.x. Epub 2007 Aug 30. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17760863 Free PMC article.
-
Higher serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate protects against the onset of depression in the elderly: Findings from the English Longitudinal Study of Aging (ELSA).Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016 Feb;64:40-6. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016. PMID: 26600009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Orentreich N, Brind J L, Vogelman J H, Andres R, Baldwin H. J Clin Endocrin Metab. 1992;75:1002–1004. - PubMed
-
- Goodyer I M, Herbert J, Altham P M E, Pearson J, Secher S M, Shiers H M. Psychol Med. 1996;26:245–256. - PubMed
-
- Herbert J, Goodyer I M, Altham P M E, Pearson J, Secher S M, Shiers H M. Psychol Med. 1996;26:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Hedman M, Nilsson E, Torre B. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992;10:25–30. - PubMed
-
- Spratt D I, Longcope C, Cox P M, Bigos S T, Wilbur-Welling C. J Clin Endocrin Metab. 1993;72:1542–1547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

