Identification and characterization of a cell membrane nucleic acid channel
- PMID: 9465118
- PMCID: PMC19214
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.4.1921
Identification and characterization of a cell membrane nucleic acid channel
Abstract
We have identified a 45-kDa protein purified from rat renal brush border membrane that binds short single-stranded nucleic acid sequences. This activity was purified, reconstituted in proteoliposomes, and then fused with model planar lipid bilayers. In voltage-clamp experiments, the reconstituted 45-kDa protein functioned as a gated channel that allows the passage of nucleic acids. Channel activity was observed immediately after addition of oligonucleotide. Channel activity was not observed in the absence of purified protein or of oligonucleotide or when protein was heat-inactivated prior to forming proteoliposomes. In the presence of symmetrical buffered solution and oligonucleotide, current passed linearly over the range of holding potentials tested. Conductance was 10.4 +/- 0.4 picosiemens (pS) and reversal potential was 0.2 +/- 1.7 mV. There was no difference in channel conductance or reversal potential between phosphodiester and phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Ion-substitution experiments documented a shift in reversal potential only when a concentration gradient for oligonucleotide was established, indicating that movement of oligonucleotide alone was responsible for current. Movement of oligonucleotide across the bilayer was confirmed by using 32P-labeled oligonucleotides. Channel open probability decreased significantly in the presence of heparan sulfate. These studies provide evidence for a cell surface channel that conducts nucleic acids.
Figures
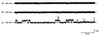

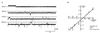


Similar articles
-
Presence of the nucleic acid channel in renal brush-border membranes: allosteric modulation by extracellular calcium.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Jul;289(1):F97-106. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00196.2004. Epub 2005 Feb 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15727991
-
Calcium regulation of a cell surface nucleic acid channel.Kidney Int Suppl. 1996 Dec;57:S4-10. Kidney Int Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8941915
-
Cytosolic malate dehydrogenase confers selectivity of the nucleic acid-conducting channel.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Feb 5;99(3):1707-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.022355499. Epub 2002 Jan 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11805283 Free PMC article.
-
Patch clamp analysis of a partially purified ion channel from rat liver mitochondria.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 28;175(1):305-10. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81235-5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991. PMID: 1705422
-
Transport of oligonucleotides across natural and model membranes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jun 29;1197(2):95-108. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(94)90001-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994. PMID: 8031827 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo SELEX for Identification of Brain-penetrating Aptamers.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013 Jan 8;2(1):e67. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2012.59. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013. PMID: 23299833 Free PMC article.
-
Driven polymer translocation through a narrow pore.Biophys J. 1999 Oct;77(4):1824-38. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77027-X. Biophys J. 1999. PMID: 10512806 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of nucleotide translocation through protein nanopores using steered molecular dynamics and an adaptive biasing force.J Comput Chem. 2014 Apr 5;35(9):692-702. doi: 10.1002/jcc.23525. Epub 2014 Jan 9. J Comput Chem. 2014. PMID: 24403093 Free PMC article.
-
Passage times for polymer translocation pulled through a narrow pore.Biophys J. 2008 Mar 1;94(5):1630-7. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.116434. Epub 2007 Oct 19. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 17951294 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction induced by immunostimulatory CpG DNA.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2000;22(1-2):97-105. doi: 10.1007/s002810050019. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2000. PMID: 10944804 Review.
References
-
- Gilkeson G S, Bernstein K, Pippen A M, Clarke S H, Marion T, Pisetsky D S, Ruiz P, Lefkowith J B. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995;76:59–67. - PubMed
-
- Messina J P, Gilkeson G S, Pisetsky D S. Cell Immunol. 1993;147:148–157. - PubMed
-
- Goodarzi G, Watabe M, Watabe K. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1992;13:221–227. - PubMed
-
- Cossum P A, Sasmor H, Dellinger D, Truong L, Cummins L, Owens S R, Markham P M, Shea J P, Crooke S. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;267:1181–1190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

