Ethylene-insensitive tobacco lacks nonhost resistance against soil-borne fungi
- PMID: 9465120
- PMCID: PMC19216
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.4.1933
Ethylene-insensitive tobacco lacks nonhost resistance against soil-borne fungi
Abstract
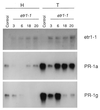
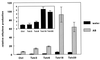
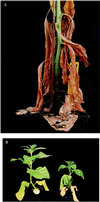
Enhanced ethylene production is an early response of plants to pathogen attack and has been associated with both resistance and susceptibility to disease. Tobacco plants were transformed with the mutant etr1-1 gene from Arabidopsis, conferring dominant ethylene insensitivity. Besides lacking known ethylene responses, these transformants (Tetr) did not slow growth when contacting neighboring plants, hardly expressed defense-related basic pathogenesis-related proteins, and developed spontaneous stem browning. Whereas hypersensitive resistance to tobacco mosaic virus was unimpaired, Tetr plants had lost nonhost resistance against normally nonpathogenic soil-borne fungi.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ethylene-insensitive tobacco shows differentially altered susceptibility to different pathogens.Phytopathology. 2003 Jul;93(7):813-21. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.2003.93.7.813. Phytopathology. 2003. PMID: 18943162
-
Ethylene insensitivity impairs resistance to soilborne pathogens in tobacco and Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2002 Oct;15(10):1078-85. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2002.15.10.1078. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2002. PMID: 12437306
-
Insight into Types I and II nonhost resistance using expression patterns of defense-related genes in tobacco.Planta. 2006 Apr;223(5):1101-7. doi: 10.1007/s00425-006-0232-1. Epub 2006 Feb 16. Planta. 2006. PMID: 16482435
-
Host versus nonhost resistance: distinct wars with similar arsenals.Phytopathology. 2015 May;105(5):580-7. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-11-14-0298-RVW. Phytopathology. 2015. PMID: 25626072 Review.
-
Nonhost resistance: how much do we know?Trends Plant Sci. 2004 Feb;9(2):97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2003.12.005. Trends Plant Sci. 2004. PMID: 15102376 Review.
Cited by
-
CRT1 is a nuclear-translocated MORC endonuclease that participates in multiple levels of plant immunity.Nat Commun. 2012;3:1297. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2279. Nat Commun. 2012. PMID: 23250427
-
The arabidopsis ISR1 locus controlling rhizobacteria-mediated induced systemic resistance is involved in ethylene signaling.Plant Physiol. 2001 Feb;125(2):652-61. doi: 10.1104/pp.125.2.652. Plant Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11161023 Free PMC article.
-
MBW complexes impinge on anthocyanidin reductase gene regulation for proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in persimmon fruit.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 26;10(1):3543. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60635-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32103143 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Clonostachys rosea-induced resistance to tomato gray mold disease in tomato leaves.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 25;9(7):e102690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102690. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25061981 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization, targeting and expression analysis of chloroplast and mitochondrion protein import components in Nicotiana benthamiana.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 26;13:1040688. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1040688. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36388587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mattoo A K, Suttle J C. The Plant Hormone Ethylene. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1991.
-
- Abeles F B, Morgan P W, Saltveit M E., Jr . Ethylene in Plant Biology. San Diego: Academic; 1992.
-
- Boller T. In: The Plant Hormone Ethylene. Mattoo A K, Suttle J C, editors. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1991. pp. 293–314.
-
- Goodman R N, Novacky A J. The Hypersensitive Reaction in Plants to Pathogens, A Resistance Phenomenon. St. Paul: American Phytopathological Society; 1994.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

